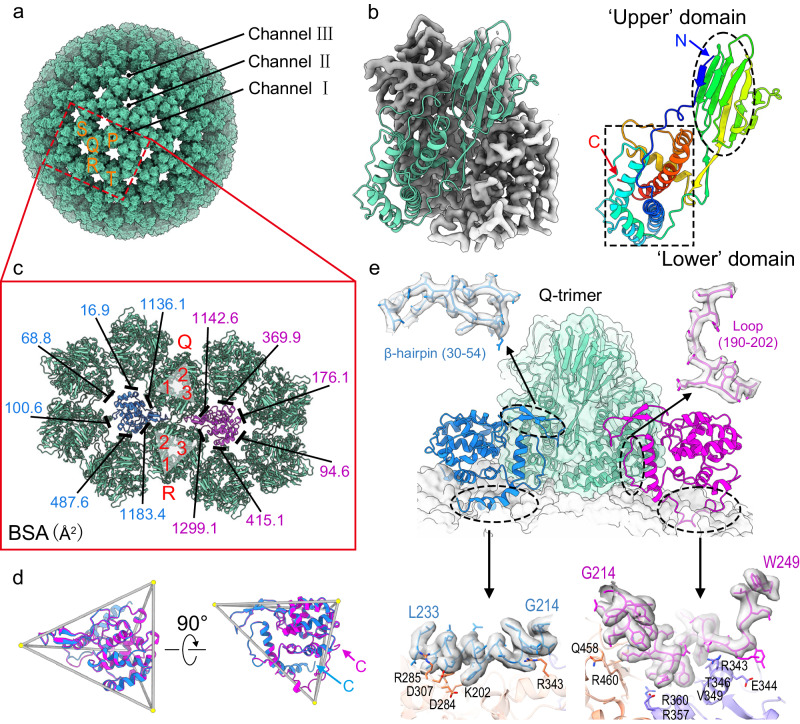
Fig. 3. VP8 and VP10.
a Based on the position of VP8 trimers in the ASU, there are five types of VP8 trimers, defined as P, Q, R, S, and T. VP8 arrangement on the outer capsid shell yields three types of channels. The type I channel is located at the icosahedral fivefold vertex. There are 60 type II channels, at the quasi-sixfold axes close to type I channels, and 60 type III channels are situated at the quasi-sixfold position close to icosahedral threefold axes. b A VP8 trimer (left) and one VP8 protomer (right). The VP8 protomer is rainbow-colored by residues from the N-terminus (blue) to the C-terminus (red). c Measurement of buried surface area on each VP8 trimer around VP10A (magenta) and VP10B (blue). Part of the VP10 conformer inserts into two neighboring VP8 trimers (labeled the Q- and R-trimers). Detailed information on the interactions between each protomer in the Q- or R-trimer and VP10A or VP10B is given in Supplementary Table 4. d Top view (from outside of the virus, left) and side view (right) of overlayed VP10A (magenta) and VP10B (blue) in a tetrahedral frame. The C-termini of VP10A and VP10B are indicated by arrows. e Side view of interactions of VP10 conformers with the ‘lower’ domains of VP8 trimers. For simplicity, only one VP8 trimer (the Q-trimer in c) is shown in ribbon representation, superimposed with its cryo-EM density. Two C-terminal tails, a β-hairpin, and a loop involved in intermolecular interactions are shown for VP10 in close-up views (superimposed with density).