Fig. 6. Postmortem validation of [18F]FES-PET ChRERa imaging in a nonhuman primate.
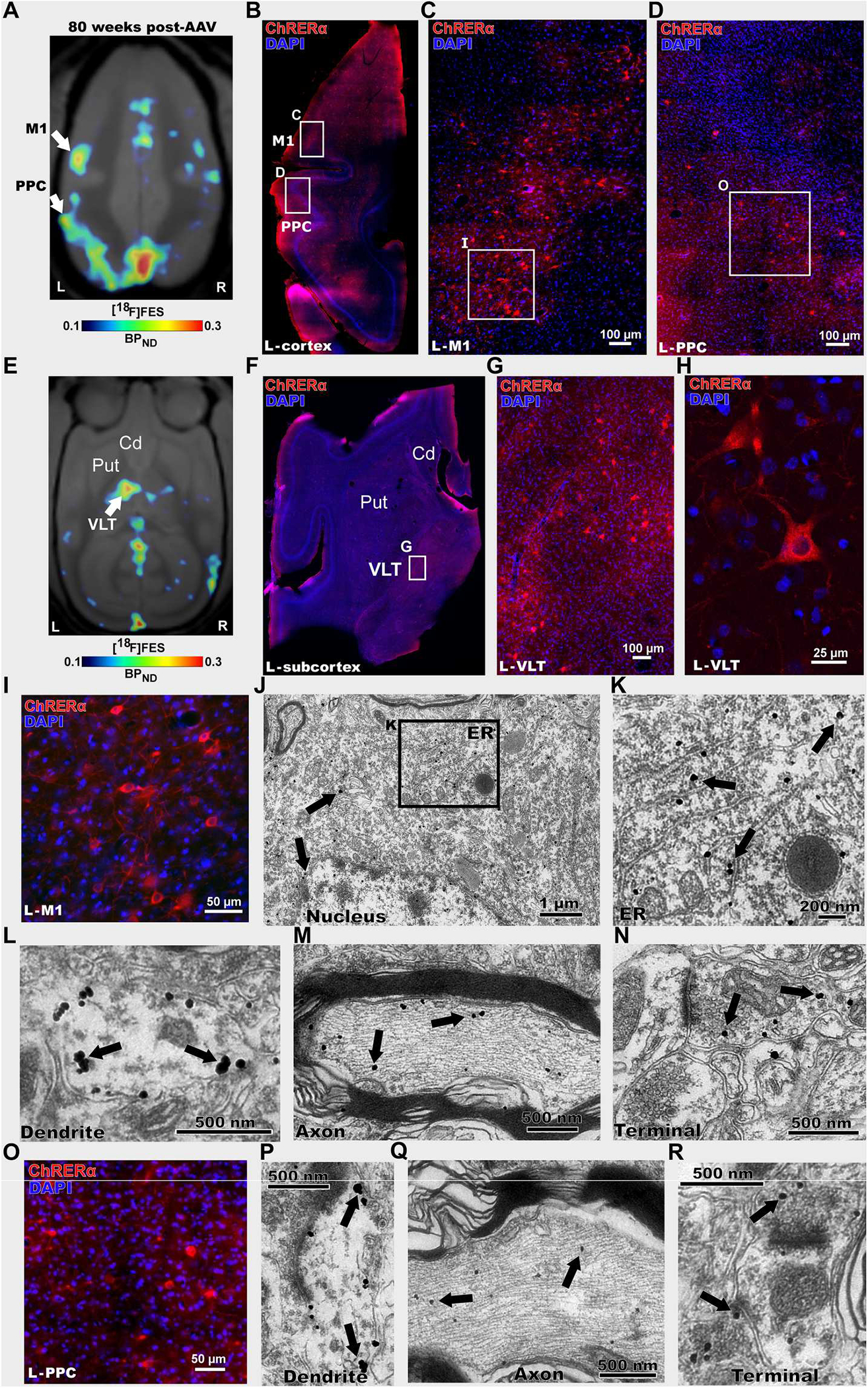
(A) [18F]FES-PET imaging 80 weeks after AAV-ChRERα injection in squirrel monkey 2 to localize ChRERα expression (BPND scaled to optimize [18F]FES signal). Arrows indicate the left M1 and PPC (B to R). (B) IHC in a left hemisphere horizontal brain slice confirms ChRERα expression in the left M1 and PPC (red = anti-ChR2 and blue = DAPI), white rectangles highlight regions in left M1 and PPC. (C and D) High magnification of images of insets shown in (B). (E) [18F]FES-PET 80 weeks after AAV-ChRERα injection in squirrel monkey 2 localized ChRERα expression in left ventral lateral thalamus (VLT) (BPND scaled to optimize [18F]FES signal). Arrow indicates left VLT (F) IHC in a left hemisphere horizontal brain slice confirms ChRERα expression in left VLT (red = anti-ChR2 and blue = DAPI), white rectangle highlights region in left VLT. (G and H) High-magnification IHC images of insets shown in (F). (I) High-magnification IHC image of left M1 (J to N) Immuno-EM in left M1 reveals subcellular localization of ChRERα expression in (J) cell body (black rectangle highlights location of (K), (K) ER, (L) dendrite, (M) myelinated axon, and (N) axon terminal. (O) High-magnification IHC image of left PPC. (P to R) Immuno-EM images in the left PPC showing ChRERα located in (P) dendrite, (Q) myelinated axon, and (R) axon terminal. Cd, caudate; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; Put, putamen.
