Figure 1.
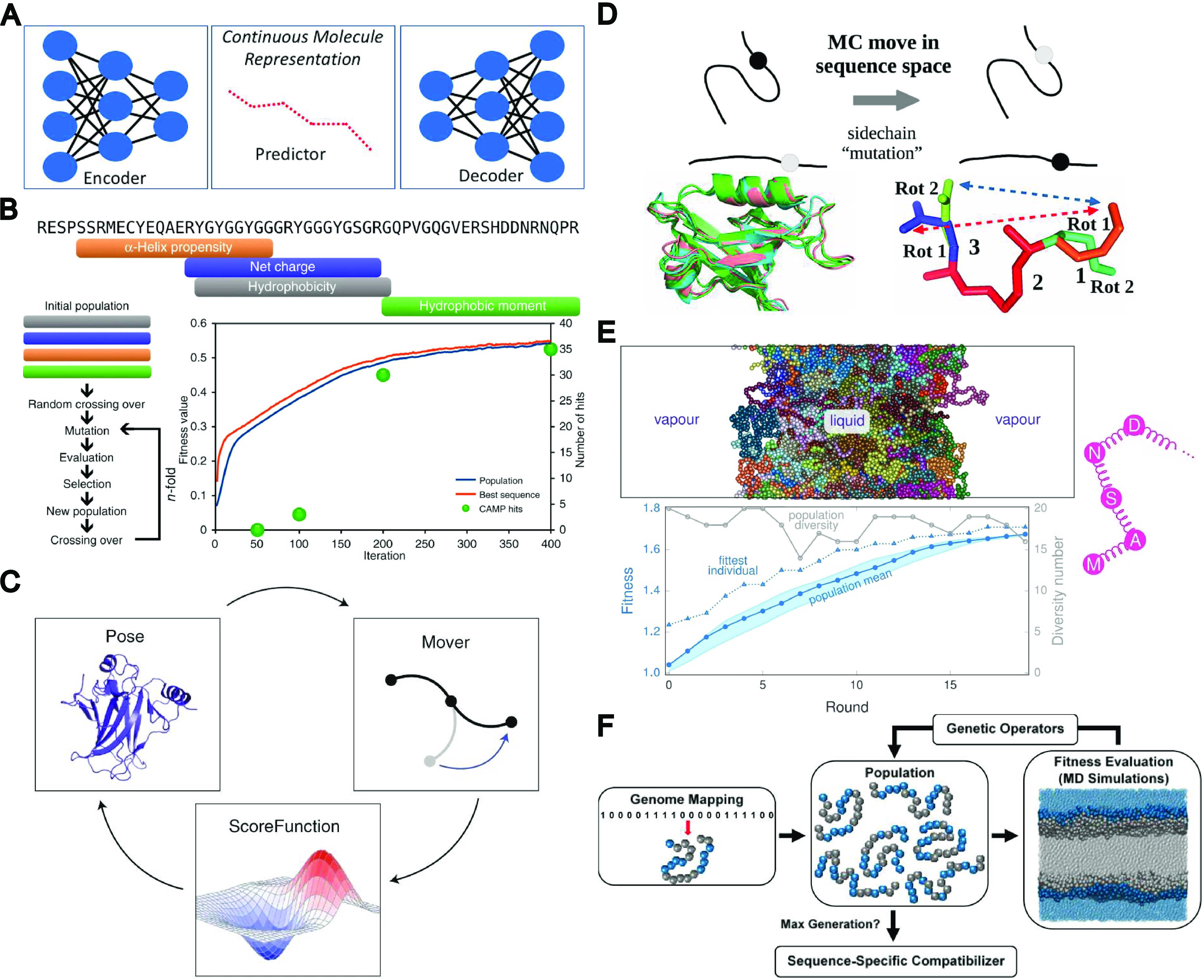
Collection of various inverse design and chemical space exploration approaches. (A) Generative model, encoding molecules of interest into a continuous latent space which can be explored to identify new molecules with similar properties. Reprinted with permission from ref (5). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. This is a commonly applied strategy in virtual screening. (B) Sequence-based genetic algorithm seeded with fragments that maximize specific physicochemical properties. Fitness values are directly calculated from sequence. Adapted from re (6). Copyright 2018 The Authors under a Creative Commons CC BY license, published by Springer Nature. (C) Simplified overview of the Rosetta protocol. Biomolecule configurations are iteratively modified and evaluated according to a prespecified scoring function of various energetic functions. Adapted with permission from ref (7). Copyright 2020 Nature Springer America, Inc. (D) Physics-based redesign of proteins using Monte Carlo and Boltzmann sampling. Adapted with permission from ref (8). Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society. (E) Combining genetic algorithms with amino-acid-scale coarse-grained MD simulations for local optimization of existing liquid–liquid phase separating proteins. Reprinted with permission from ref (9). Copyright 2021 The Authors under Creative Commons Attribution International license, published by PLOS. (F) Combining genetic algorithms with MD simulations using a binary coarse-grained copolymer model for de novo optimization of copolymer compatibilizers. Reprinted with permission from ref (10). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society.
