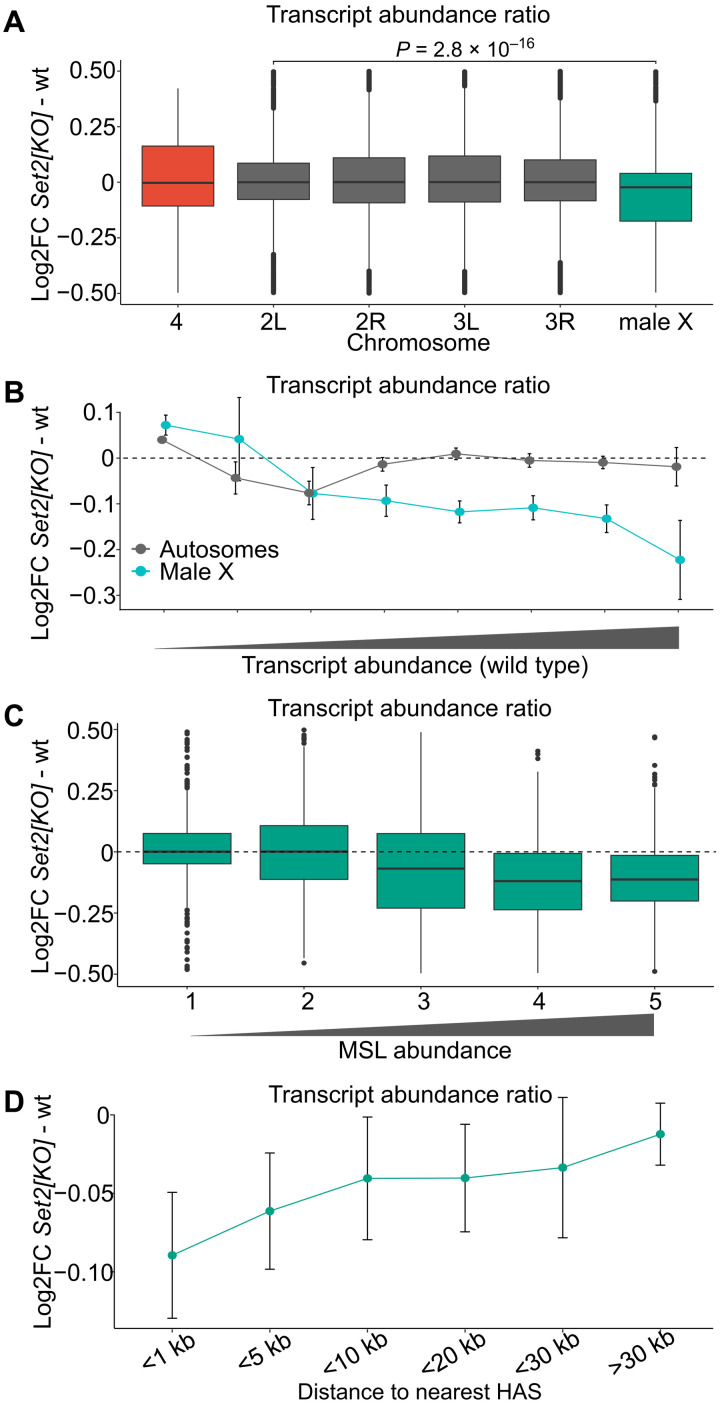
Fig. 2. Set2 is required for balanced transcription output from the single male X chromosome.
(A) Box plots of chromosome-specific transcript abundance ratios (log2 fold change) between Set21 and wild type for chromosome 4 (red), X chromosome (green), and the autosome arms (gray). The abundance of transcripts from X chromosome of the Set21 mutant is significantly reduced as compared to the autosomes. The likelihood that observed differences are due to chance was evaluated by unpaired two-sample Wilcoxon tests comparing values for the X chromosome and chromosome arm2L (the most similar autosome arm). (B) Transcript abundance in Set21 versus wild type plotted as fold change (log2). Genes were binned according to Flybase RNA-seq expression level intervals. The X chromosome genes with higher transcriptional output in the wild type are significantly more affected compared to those on autosomes. (C) Box plots of average transcript abundances of the X-chromosomal genes in Set21 versus wild type. The genes are grouped in equally sized bins based on their MSL1-binding strength; 1 (lowest) to 5 (highest). Genes with higher MSL1 levels show greater fold change compared to genes with no or low amounts of MSL1 bound. (D) Average log2 fold change for X-chromosomal genes binned by distance to HASs. In (B) and (D), the error bars indicate the 95% confidence intervals.