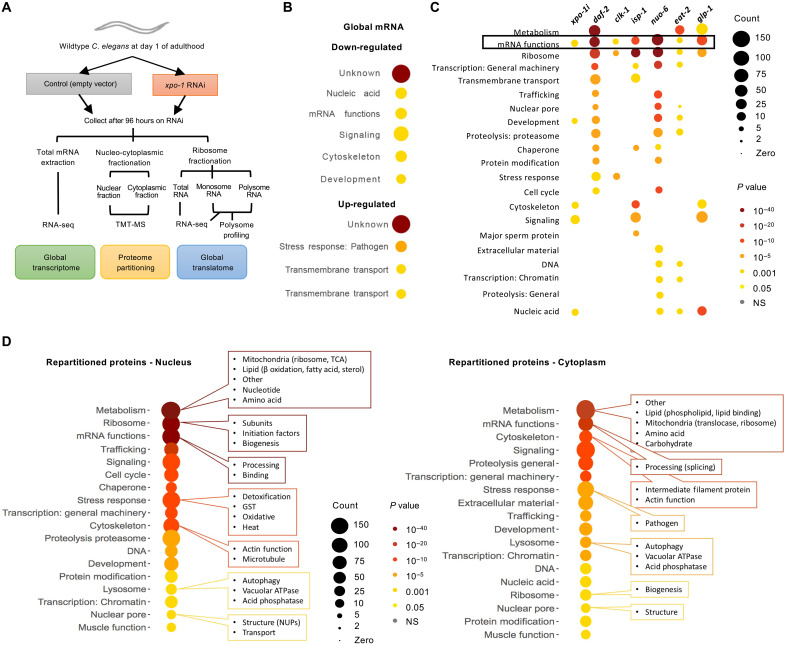
Fig. 1. xpo-1 silencing down-regulates expression of genes involved in protein synthesis and alters nucleocytoplasmic protein partitioning.
(A) Schematic illustrating the omics approaches taken to study molecular changes in nematodes with nuclear export inhibition. (B) GO categories of differentially regulated genes significantly enriched upon xpo-1 RNAi compared to control after 96 hours using WormCat database (16). See data file S1 for complete list of significant differentially regulated transcripts and fig. S1 (A to C) for principal components analysis (PCA), volcano plots, and heatmaps. (C) Comparison of GO categories of significantly down-regulated genes from long-lived mutants (17, 18) with those for xpo-1 RNAi from this study. (D) Protein GO categories and subcategories that are either enriched in nuclear and non-nuclear (cytoplasmic) fractions after 96 hours of xpo-1 RNAi compared to control. See fig. S1D for purity of fractions and data file S2 for complete list of significant repartitioned proteins. NS, not significant.