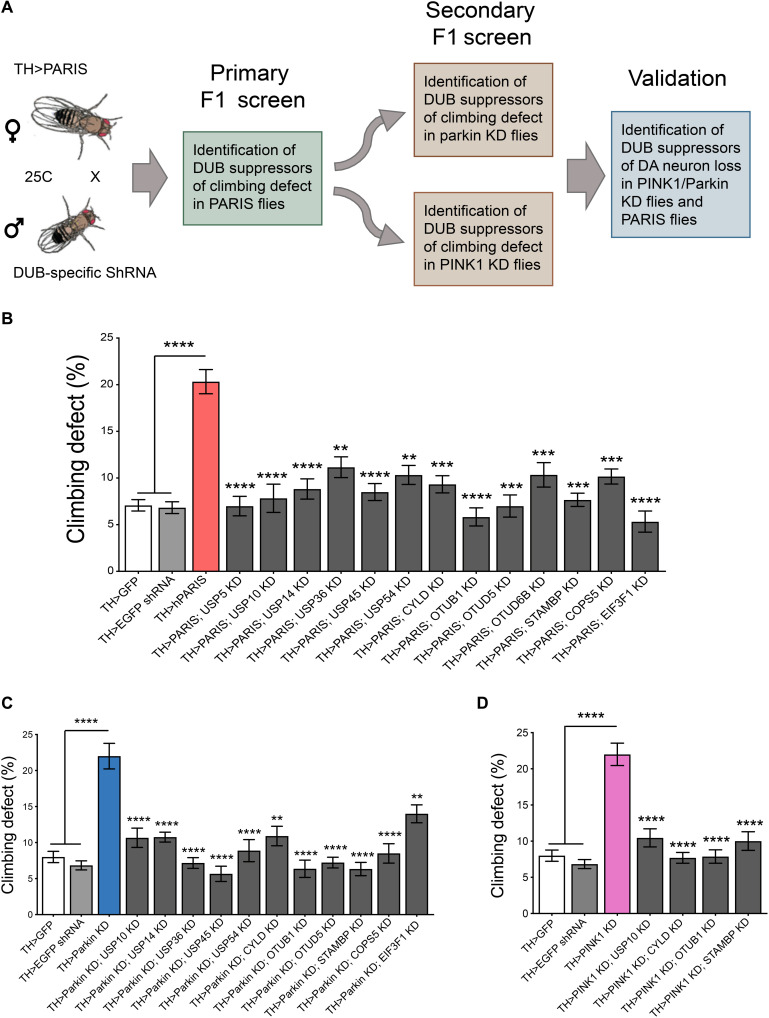
Fig. 1. Genome-wide RNAi screen to identify candidate DUBs that function in PINK1/parkin pathway.
(A) Schematic of the screen. TH-Gal4–driven DUB-specific RNAi fly lines were used in an F1 primary screen to identify DUBs that rescued hPARIS-induced climbing defects on day 20. Such candidate DUBs were subjected to additional secondary F1 screens probing for DUBs that rescued climbing defects under conditions of DA parkin or PINK1 KD on day 20, respectively. Hits from the secondary screen were then examined for their ability to promote dopamine neuron survival in 20-day-old parkin or PINK1 KD flies. (B) Primary F1 screen based on rescue of PARIS-induced climbing defect identified 13 DUBs. (C) Summary of candidate DUBs from primary screen that rescued climbing defects in parkin KD flies. (D) Summary of candidate DUBs from primary screen that suppressed climbing defects in PINK1 KD flies and progressed for further validation. TH-Gal4/+ flies served as control. N = 60 flies per genotype for both primary and secondary screens. Quantitative data = means ± SEM. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA); **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. See also figs. S1 and S2 and table S1.