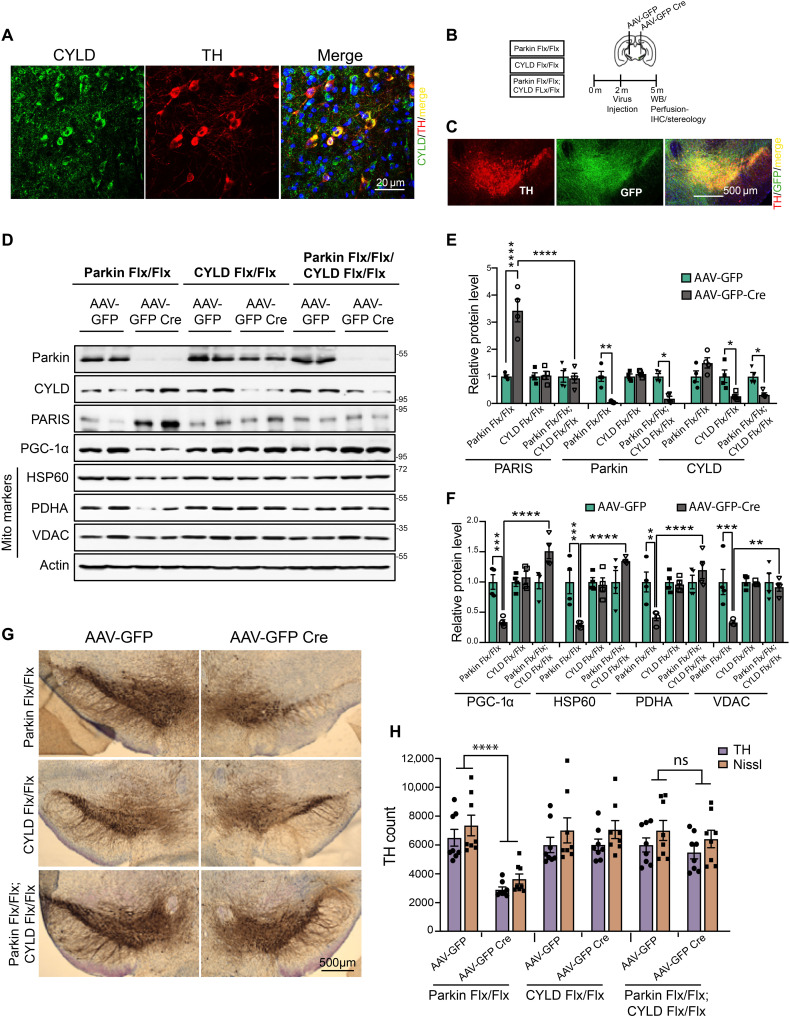
Fig. 6. CYLD KD prevents DA neurodegeneration in adult conditional parkin KD mice.
(A) Representative confocal images showing CYLD coexpression in TH-immunostained SN dopamine neurons in midbrain sections from WT C57BL/6 mice. Scale bar, 20 μM. (B) Schematic of experimental schedule following stereotaxic injection with AAV-GFP or AAV-GFP Cre in SN of 2-month-old C57BL6 mice of indicated genotype. (C) Representative immunofluorescence images verifying stereotaxic injection quality. Scale bar, 500 μM. (D) Representative immunoblots of indicated proteins in ventral midbrain lysates from adult mice harboring conditional KD of parkin, CYLD, or a combination of parkin and CYLD. (E) Relative quantification of PARIS, parkin, and CYLD in ventral midbrain lysates from floxed mice of indicated genotypes stereotaxically injected with AAV-GFP or AAV-GFP-Cre. Mean values from four independent stereotaxic injections in each case shown. (F) Relative quantification of PGC-1α and the indicated mitochondrial proteins in ventral midbrain lysates as shown in (C). N = 4 independent stereotaxic injections with AAV-GFP or AAV-GFP-Cre. (G) Representative TH immunostaining of midbrain sections from SN of mice homozygous for the floxed parkin, CYLD, or parkin; CYLD alleles injected with AAV-GFP or AAV-GFP-Cre. (H) Stereotaxic assessment of TH- and Nissl-positive neurons in the SN pars compacta (SNpc) of indicated injection groups (N = 8 unilaterally injected mice per group). Quantitative data = means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. See also fig. S6.