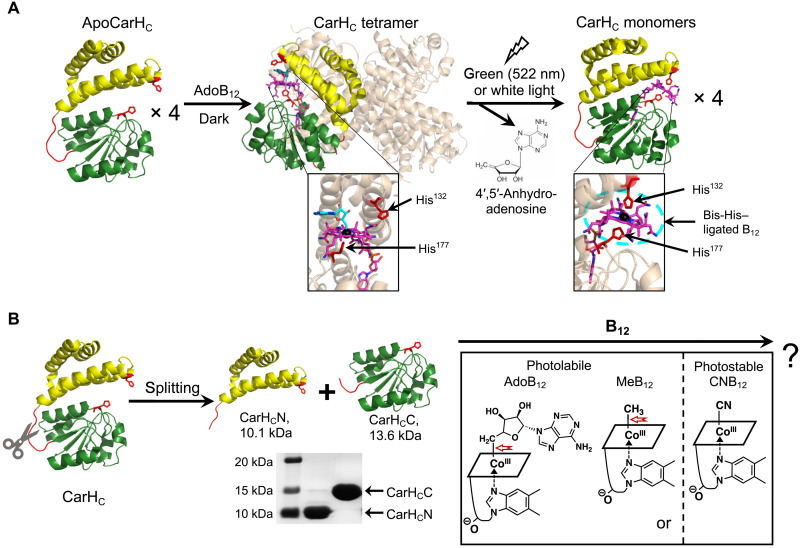
Fig. 1. Dissection of the B12-dependent photoresponsive CarHC protein.
(A) Photochemistry of CarHC. CarHC monomers, upon binding to AdoB12, assemble into a tetramer, which further disassembles into monomers on light exposure, accompanied with the photolysis of AdoB12, the release of 4′,5′-anhydroadenosine, and the coordination of His132 to the cobalt center in B12. The bottom panel shows close-up views of the cofactor binding pocket. For clarity, three monomers in the CarHC tetramer complex are in high transparency, with AdoB12 hidden. Monomeric CarHC is shown with the N-terminal four-helix bundle in yellow, the unstructured loop region in red, and the C-terminal B12-binding domain in green. (B) Schematic showing the dissection of CarHC at the loop region into CarHCN and CarHCC, and their possible reassembly with various cobalamins, such as AdoB12, MeB12, or CNB12. The SDS-PAGE analysis shows successful production of CarHCN (calculated MW, 10.1 kDa) and CarHCC (calculated MW, 13.6 kDa) by E. coli expression. The structure of B12 is presented as a simplified parallelogram for clarity. The light-sensitive cobalt-carbon bond is highlighted by a red arrow. ApoCarHC and monomeric CarHC: Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID code, 5C8F; tetrameric CarHC: PDB ID code, 5C8A.