Figure 2.
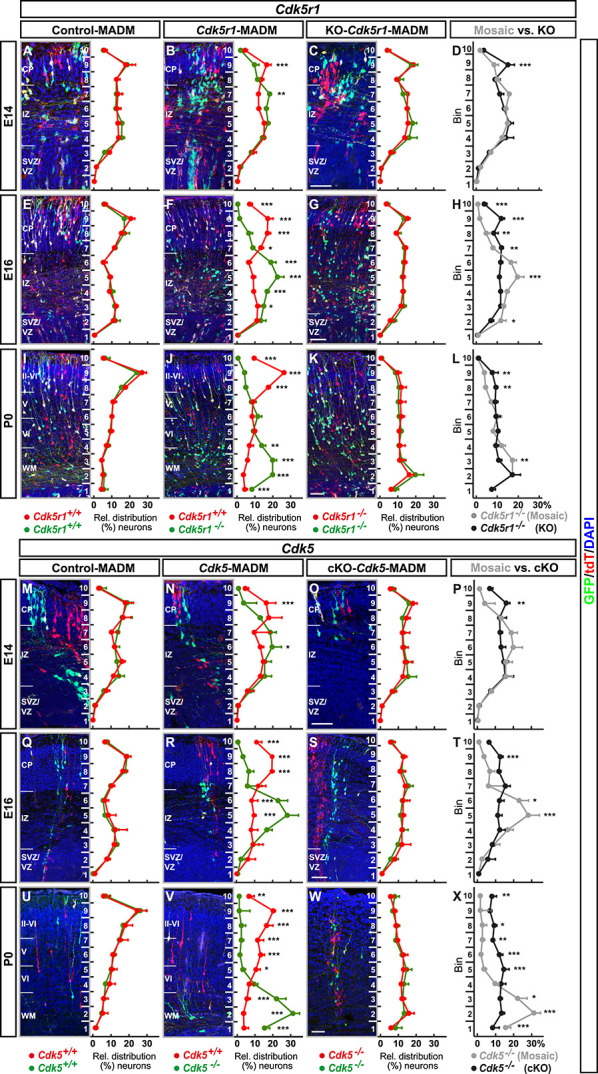
Developmental time course analysis of MADM-based sparse and global KO of p35/CDK5. (A–L) Analysis of green (GFP+) and red (tdT+) MADM-labeled projection neurons in (A, E, I) control-MADM (MADM-11GT/TG;Emx1Cre/+); (B, F, J) Cdk5r1-MADM (MADM-11GT/TG,Cdk5r1;Emx1Cre/+); and (C, G, K) KO-Cdk5r1-MADM (MADM-11GT,Cdk5r1/TG,Cdk5r1; Emx1Cre/+) at E14 (A–D), E16 (E–H) and P0 (I–L). Relative distribution (%) of MADM-labeled projection neurons is plotted in ten equal zones across the developing cortical wall. (D, H, L) Direct distribution comparison of Cdk5r1−/− mutant cells at E14 (D), E16 (H) and P0 (L) in Cdk5r1-MADM (grey) versus KO-Cdk5r1-MADM (black) distribution. (M–X) Analysis of green (GFP+) and red (tdT+) MADM-labeled projection neurons in (M, Q, U) control-MADM (MADM-11GT/TG;Emx1Cre/+); (N, R, V) Cdk5-MADM (MADM-11GT/TG,Cdk5;Emx1Cre/+); and (O, S, W) KO-Cdk5-MADM (MADM-11GT,Cdk5/TG,Cdk5; Emx1Cre/+) at E14 (M–P), E16 (Q–T) and P0 (U–X). Relative distribution (%) of MADM-labeled projection neurons is plotted in 10 equal zones across the developing cortical wall. (P, T, X) Direct distribution comparison of Cdk5−/− mutant cells at E14 (P), E16 (T), and P0 (X) in Cdk5-MADM (grey) versus KO-Cdk5-MADM (black) distribution. Nuclei were stained using DAPI (blue). N = 3 for each genotype with 10 (MADM-11) and 20 (MADM-5) hemispheres analysed. Data indicate mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. Cortical plate (CP), intermediate zone (IZ), subventricular zone/ventricular zone (SVZ/VZ), cortical layers (II–VI), white matter (WM). Scale bars: 100 μm.
