Figure 8.
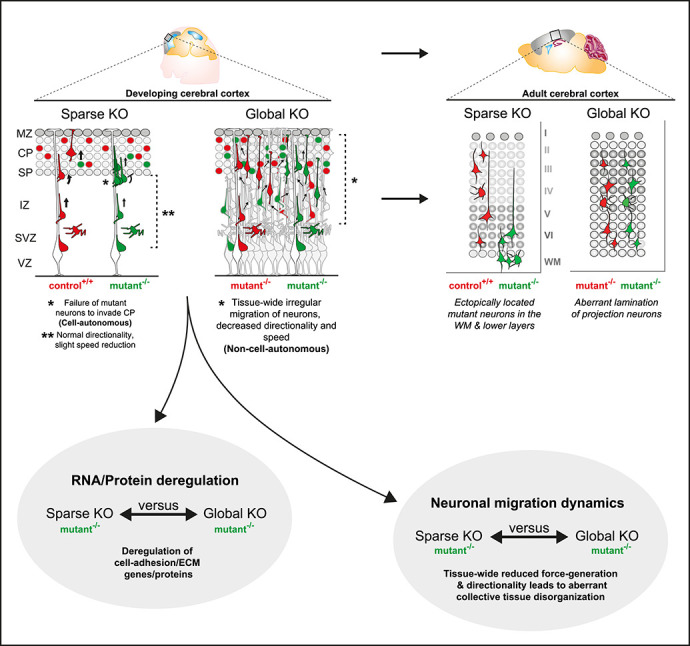
Interplay of cell-autonomous and global tissue-wide properties in cortical projection neuron migration. Schematic illustrating the MADM-based subtractive phenotypic analysis of sparse genetic mosaics (control background) and global knockout (cKO/KO) (mutant background), both coupled with fluorescent MADM-labeling of homozygous mutant and control neurons. Such assay enabled the high-resolution analysis of projection neuron migration dynamics in distinct genetic environments with concomitant isolation of genomic and proteomic profiles. In combination with computational modeling, we utilized these experimental paradigms to visualize non-cell-autonomous effects in radial neuron migration at single-cell resolution. In sparse KO, mutant neurons migrated more dynamically and expressed cell adhesion molecules similar like in control. However, in global KO, we observed that cell adhesion molecules were significantly downregulated. Mutant neurons in global KO also showed much more severe migration phenotype resulting in drastic disorganization of the mature cortical wall.
