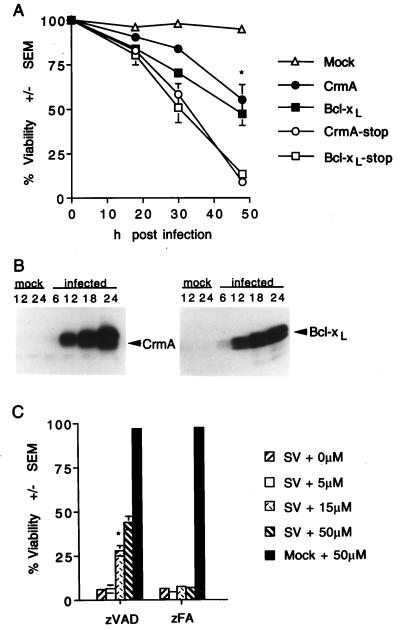
FIG. 2.
CrmA and zVAD-FMK protect BHK cells from Sindbis virus-induced cell death. (A) BHK cells were mock infected or infected with recombinant Sindbis viruses encoding the indicated genes, and cell viability was determined at the indicated times by trypan blue exclusion. Data from three to nine independent experiments are shown. Error bars (indication standard deviations) are hidden by the symbol at some time points. (B) Immunoblots of N18 cells infected with recombinant viruses encoding CrmA (left) or Bcl-xL (right). Cells were harvested at the indicated times (in hours) postinfection, and equal amounts of protein were analyzed by SDS–15% PAGE. Similar results were obtained with BHK cells (data not shown). (C) The viabilities of Sindbis virus (AR339)-infected BHK cells treated with zVAD-FMK or zFA-FMK at the indicated concentrations were determined by trypan blue exclusion at 48 h postinfection. The results summarize data from three to eight independent experiments. The asterisk indicates a statistically significant difference upon comparison of the viability of each recombinant virus with that of its corresponding stop construct in panel A and upon comparison of the viability of cells treated with 15 μM zVAD-FMK with that of the other categories in panel C (P < 0.05 by Student’s t test).