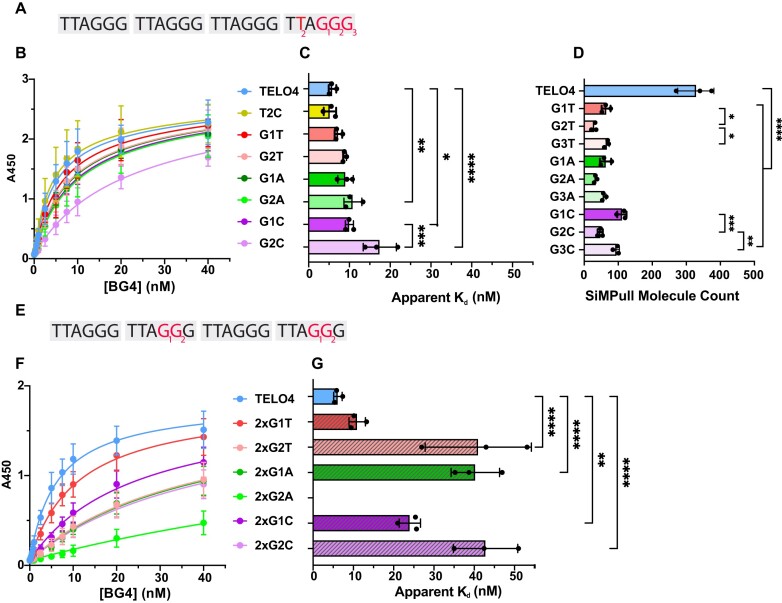
Figure 3.
Base substitution type and location determine the impact on BG4 affinity. Constructs are based on TELO4 and named according to the base substitution present in the fourth repeat (A) or the second and fourth repeats (E) at the G1, G2 or G3 positions. Complete sequences shown in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2. ELISA binding curves for telomeric constructs containing a single (B) or double (F) base substitution. BG4 binding is represented by absorbance at 450nm vs. the BG4 concentration (nM). (C) and (G) apparent dissociation constants (Kd) were calculated from the nonlinear regression curves shown in (B) and (F), respectively. Data are mean ± SD from independent experiments; ordinary one-way ANOVA. (D) Quantification of SiMPull counts of BG4 binding events with telomeric constructs containing a single base substitution in the fourth repeat. TELO4 data from Figure 1E. Data are mean ± SD from three independent experiments; ordinary one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.1, **P< 0.01, ****P< 0.0001.