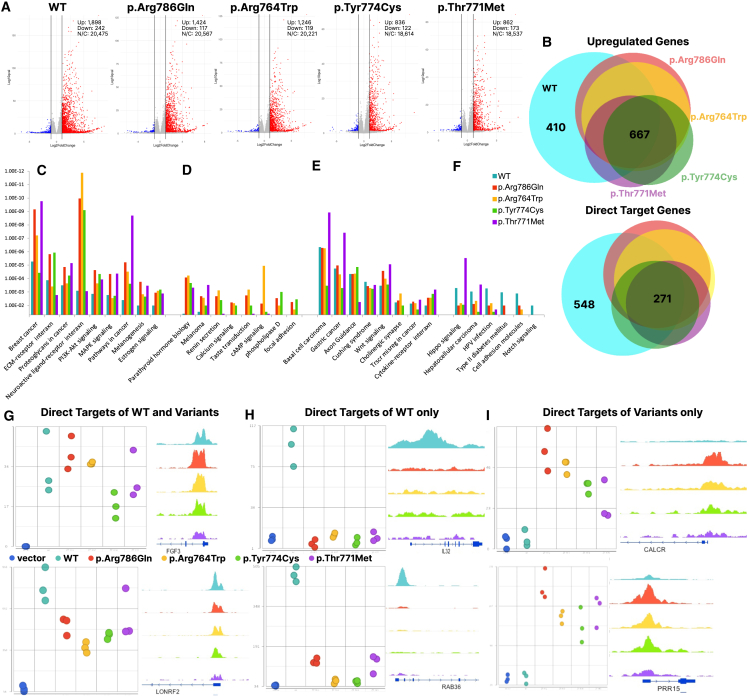
Figure 5.
Characterization of differential expression in the context of missense ZFX variants
(A) Gene expression changes following transfection of WT or variant ZFX proteins into DKO cells. Volcano plots show gene expression changes in cells transfected with plasmids expressing the indicated ZFX compared to transfection with the vector alone. RNAs with increased expression are shown by red dots, RNAs with decreased expression are shown by blue dots; cut-offs used were a 2-fold change in expression and a q value < 0.05. The numbers of RNA with increased (Up), decreased (Down), and no change (N/C) in expression are displayed.
(B) Top: Overlap analysis of all genes activated by WT and variant ZFX proteins. The numbers of genes induced by all five proteins (667) and only by WT ZFX (410) are indicated. Bottom: Overlap analysis of direct targets activated by WT and variant ZFX proteins. The numbers of direct targets common to all five proteins (271) and direct targets unique to WT ZFX (548) are indicated.
(C–F) KEGG pathway analysis using the direct targets of WT and variant ZFX proteins. The top significant pathways are organized into four groups: (C) pathways more highly enriched in the set of genes regulated by the variant ZFXs than in the set of genes regulated by WT ZFX, (D) pathways only identified in sets of genes regulated by the variant ZFX proteins, (E) pathways enriched in both variant and WT gene sets, and (F) pathways enriched more in the sets of genes regulated by WT ZFX. Significance is plotted on the y axis.
(G–I) Examples of differences in expression and binding patterns of direct targets for WT ZFX vs. variant ZFX proteins; left panels show the expression level of the gene (values on the y axis represent normalized read counts mapping to all gene transcripts) in cells transfected with the WT and mutant ZFX proteins, whereas right panels show the ChIP-seq signals (browser shots) of the different ZFX WT and mutant constructs at the promoter of that gene. (G) Direct targets of both WT and variant ZFX, (H) direct targets of WT ZFX only, and (I) direct targets only of variant ZFX proteins.