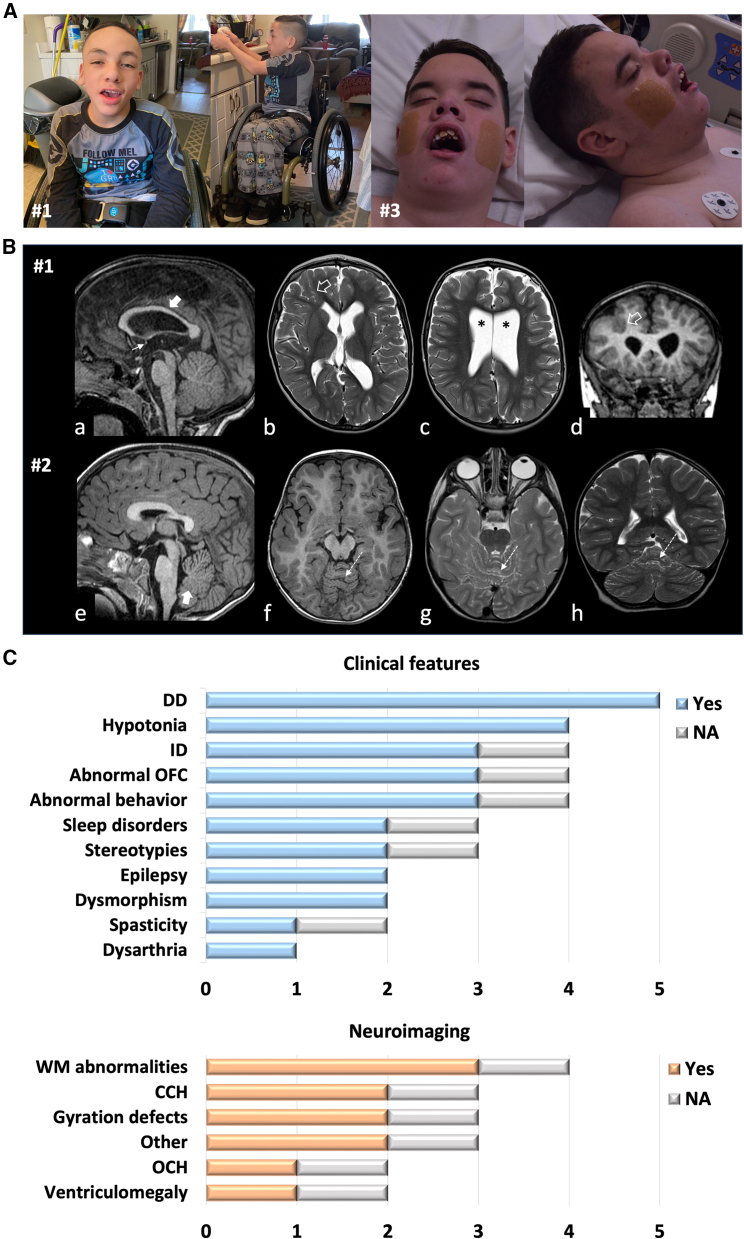
Figure 2.
Clinical and neuroimaging details of subjects harboring DENND5B variants
(A) Clinical photographs of subjects harboring DENND5B variants. Subject #1 shows macrocephaly, mild intellectual disability, axial hypotonia, and appendicular spasticity. Facial dysmorphism includes arched and sparse eyebrows, narrow palpebral fissures, hypertelorism, bulbous nose tip, deep nasal bridge, thick lower lip, and prominent chin. Subject #3 has severe cognitive deficiency, microcephaly, and hypotonia. Dysmorphic features include short nose, hypertelorism, malposition of teeth, deep nasal bridge, deep philtrum, and micrognathia.
(B) Neuroimaging findings. (a–d) Brain MRI of subject #1 with sagittal T1-weighted (a), axial T2-weighted (b, c), and coronal T1-weighted (d) showing a thin corpus callosum (thick arrow), a small anterior commissure (thin arrow), white matter volume loss with ventricular enlargement (asterisks), and a focal gyral anomaly with infolding in the right frontal lobe (empty arrows). (e–h) Brain MRI of subject #2 with sagittal T1-weighted (a), axial T1-weighted (b), axial T2-weighted (c), and coronal T2-weighted (d) revealing focal foliar anomaly in the superior cerebellar vermis (dashed arrows) associated with inferior vermis hypoplasia (thick arrow).
(C) Histogram graphs showing the distribution of clinical features and brain MRI abnormalities in the cohort of subjects harboring DENND5B variants. Abbreviations: CCH, corpus callosum hypoplasia; DD, developmental delay; ID, intellectual disability; NA, not available; OCH, optic chiasm hypoplasia; OFC, occipito-frontal circumference; WM, white matter.