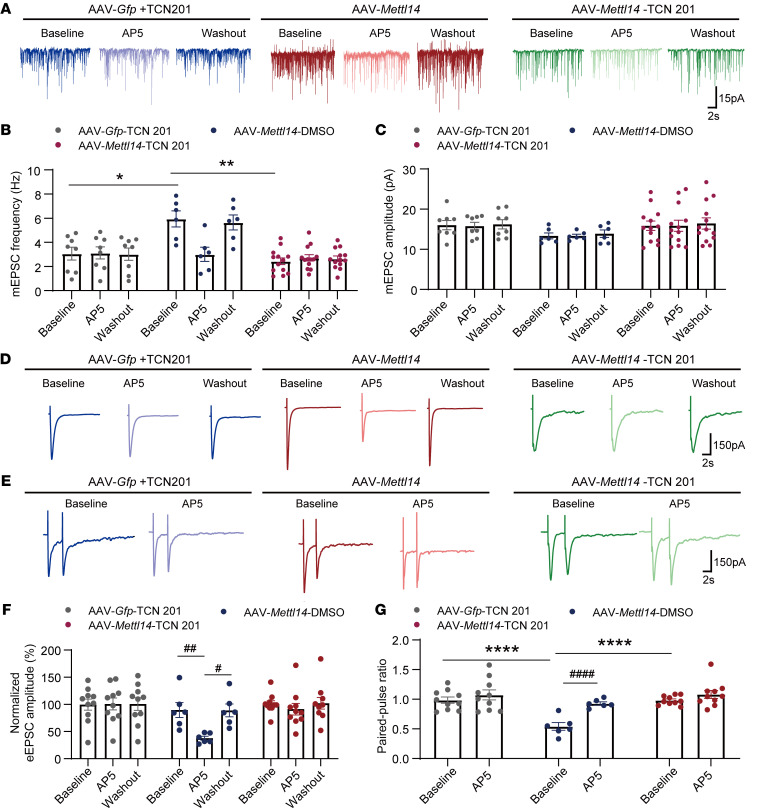
Figure 7. METTL14 overexpression increases GluN2A-mediated presynaptic NMDAR hyperactivity in the spinal cord.
(A–C) Representative recording traces and quantification showing the effect of bath application of AP5 on the frequency and amplitude of mEPSCs of lamina II neurons from naive rats after AAV-Mettl14 or AAV-Gfp pretreatment combined with intrathecal injection of TCN 201 (at least 6 neurons from 3 rats per group; 2-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). (D) Representative recording traces show the effect of bath application of AP5 on the normalized amplitude of evoked mEPSCs of a lamina II neuron evoked from the dorsal root in naive rats after AAV-Mettl14 or AAV-Gfp pretreatment combined with intrathecal injection of TCN 201. (E) Representative recording traces show the effect of bath application of AP5 on EPSCs evoked by a pair of pulses of a lamina II neuron evoked from the dorsal root in naive rats after AAV-Mettl14 or AAV-Gfp pretreatment combined with intrathecal injection of TCN 201. (F and G) Bar plots show the change in the normalized amplitude of evoked mEPSCs (F) and the PPR of evoked EPSCs (G) during baseline control and bath application of AP5 in naive rats after AAV-Mettl14 or AAV-Gfp pretreatment combined with intrathecal injection of TCN 201 (at least 3 rats, 6 neurons per group; #compared with the respective baseline control, *compared with the baseline in the vehicle-treated group; 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was performed in each group for the normalized amplitude of evoked mEPSCs, 2-way ANOVA followed by Šidák’s post hoc test between groups for PPR). Data are shown as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ####P < 0.0001.