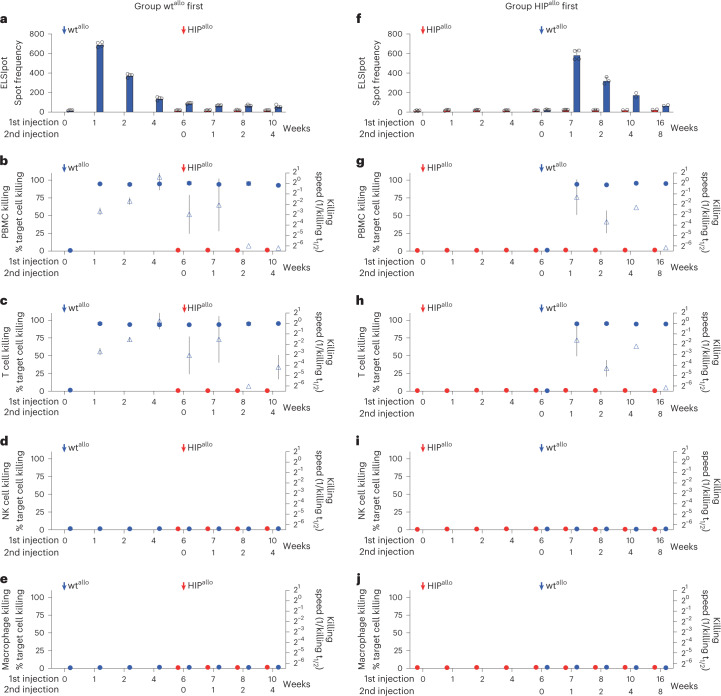
Fig. 1. Cellular immune responses against allogeneic rhesus macaque wt and HIP grafts.
a–e, Immune assays in the group receiving wtallo first. ELISpot assays with recipient monkey PBMCs drawn at scheduled timepoints (a, mean ± s.d., four monkeys). Killing assays with recipient monkey PBMCs (b), T cells (c), NK cells (d) and macrophages (e). Percent target cell killing is shown on the left y axis (mean ± s.d.), and killing speed is shown on the right y axis (killing t1/2−1, mean ± s.e.m., four monkeys). f–j, Immune assays in the group receiving HIPallo first. ELISpot assays with recipient monkey PBMCs (f, mean ± s.d., four monkeys at weeks 0–7, three monkeys at week 8 and two monkeys at weeks 10–16). Killing assays with recipient monkey PBMCs (g), T cells (h), NK cells (i) and macrophages (j). Percent target cell killing is shown on the left y axis (mean ± s.d.), and killing speed is shown on the right y axis (killing t1/2−1, mean ± s.e.m., four monkeys at weeks 0–7, three monkeys at week 8 and two monkeys at weeks 10–16). All assays run against wtallo and HIPallo are shown in blue and red, respectively, at 6 weeks, and, later, all assays were run against both cell types.