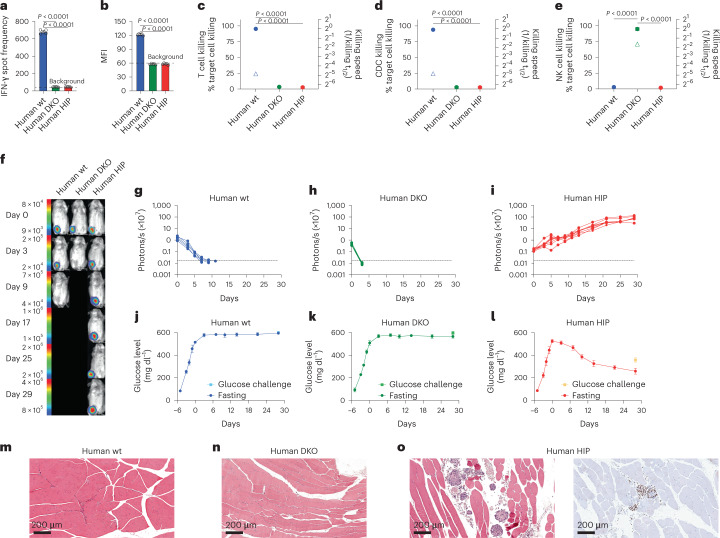
Fig. 5. Human HIP islets survive in immunocompetent allogeneic humanized mice and ameliorate diabetes.
a–e, One million wt, DKO or HIP islet cells were injected into the thigh muscle of allogeneic humanized NSG-SGM3 mice. After 6 d, the immune response against the graft cells was assessed. IFN-γ ELISpot assays with mouse splenocytes were performed to assess the adaptive immune response against the islet grafts (a, mean ± s.d., three animals per group, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). Serum DSAs of IgM type were quantified by flow cytometry (b, mean ± s.d., three animals per group, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). Impedance killing assays of islet cells with recipient mouse T cells (c, mean ± s.d., three animals per group, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test) or serum (d, mean ± s.d., three animals per group, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). Human NK cells were used for this impedance killing assay of islet cells (e, mean ± s.d., triplicates, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). f–i, Humanized NSG-SGM3 mice received streptozotocin and developed diabetes (f, one representative mouse is shown per group). Six days later, 1,000 FLuc+ allogeneic wt (g, five animals), DKO (h, five animals) or HIP islet clusters (i, eight animals) were injected intramuscularly, and their survival was monitored with BLI (all individual animals are shown). j–l, Serial fasting blood glucose levels were quantified (mean ± s.d.) in the wt (j, five animals), DKO (k, five animals) or HIP (l, eight animals) groups. On day 30, animals underwent a glucose challenge with blood draw 30 min later (mean ± s.d.). m–o, The injection sites of wt (m), DKO (n) or HIP islet clusters (o) were recovered and stained with H&E and for ISL-1 by immunohistochemistry (representative images).