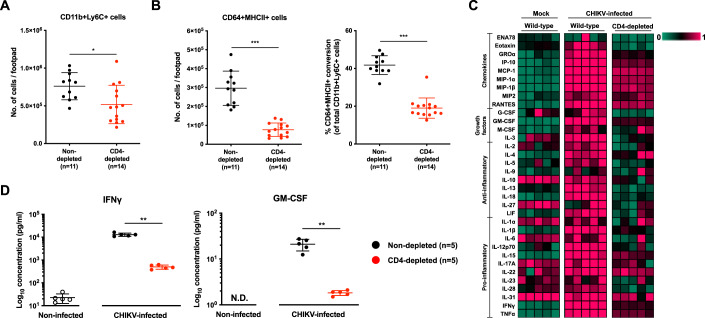
Figure 4. CD4+ T cells depletion alters levels of critical immune mediators in the CHIKV-infected joint-footpad.
(A,B) Wild-type animals were infected with 1 × 106 PFU of CHIKV in the right footpad, and anti-CD4 antibodies were given intraperitoneally at -1 and 4 days post-infection (dpi). Immunophenotyping was performed at 6 dpi to determine the numbers of infiltrating CD11b+Ly6C+ monocytes in CD4-depleted joint-footpads (A). Percentage differentiation of CD11b+Ly6C+ monocytes into CD64+MHCII- and CD64+MHCII+ macrophages and absolute counts of CD64+MHCII+ macrophages in CHIKV-infected non-CD4-depleted or CD4-depleted animals (B). Data presented were from biological replicates obtained from two independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. Data comparisons between the groups were performed with non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test (two-tailed). For CD1b+Ly6C+ (A), *P = 0.0152; For CD64+MHCII+ (B), *P = 0.000000449; for CD64+MHCII+ conversion (B), ***P = 0.000000897. (C,D) Joint lysates were obtained from CHIKV-infected CD4-depleted, infected wild-type (non-CD4-depleted) mice, and mock-infected control mice at peak chikungunya joint pathology (6 dpi). A multiplex microbead-based assay was used to quantify the levels of immune mediators present in these samples. Heatmap showing the levels of the analyzed immune mediators in each group of animals (C). Dot plots showing the absolute quantities of IFNγ and GM-CSF, highlighting the significant differences between the various groups of animals (D). Data were from biological replicates and presented as mean ± SD. Data comparisons between the groups were performed with non-parametric Mann–Whitney U test (two-tailed). IFNγ, **P = 0.0079; GMCSF, **P = 0.0079. Source data are available online for this figure.