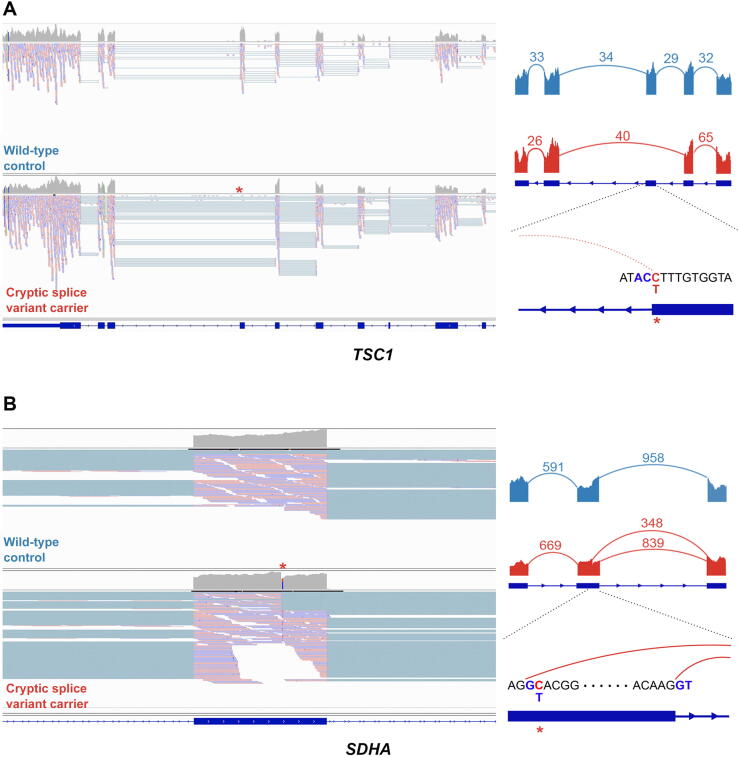
Fig. 5.
Examples of cryptic splice variants in established RCC risk genes. (A) Disruption of splice donor motif led to complete exon skipping in TSC1. (B) The cryptic splice variant in SDHA introduced a new splice donor motif GT inside an exon. Images at the left represent IGV screenshots of the tumor mRNA sequencing data of the wild-type control (Fig. 5A) and the carrier of cryptic splice variant (Fig. 5B). Images at the right represent Sashimi plots showing the pattern of splicing with the numbered split junction reads. IGV = Integrative Genomics Viewer; RCC = renal cell carcinoma.