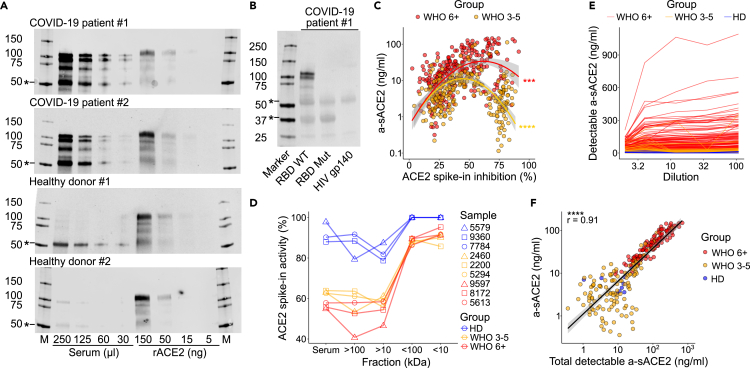
Figure 2.
A large fraction of serum sACE2 is inactive and binds the SARS-CoV-2 spike
(A) ACE2 was pulled down from indicated volumes of serum from patients and HDs using RBD-coupled beads. Recombinant ACE2 (rACE2) was loaded as control. Markers (M) in kDa. ∗Unspecific bands.
(B) Specificity confirmed by a mutant RBD (A475R/G496R) lacking ACE2 binding and by an HIV gp140 control.
(C) Percent inhibition (%) of 50 ng/mL rACE2 after addition to serum plotted against a-sACE2. Significance indicates a likelihood ratio test to compare a two-degree polynomial model with linear regression for moderate or severe COVID-19.
(D) Activity of rACE2 spike-in (%) determined in serum fractions collected after ultrafiltration with indicated cut-off values.
(E) Determination of a-sACE2 in indicated reciprocal serum dilutions.
(F) Pearson correlation with a 95% confidence interval of a-sACE2 in undiluted samples and maximum a-sACE2 detected after serum dilution. (C), (E), and (F) include measurements of repeated longitudinal blood drawings. For gel source data, see Figure S11.