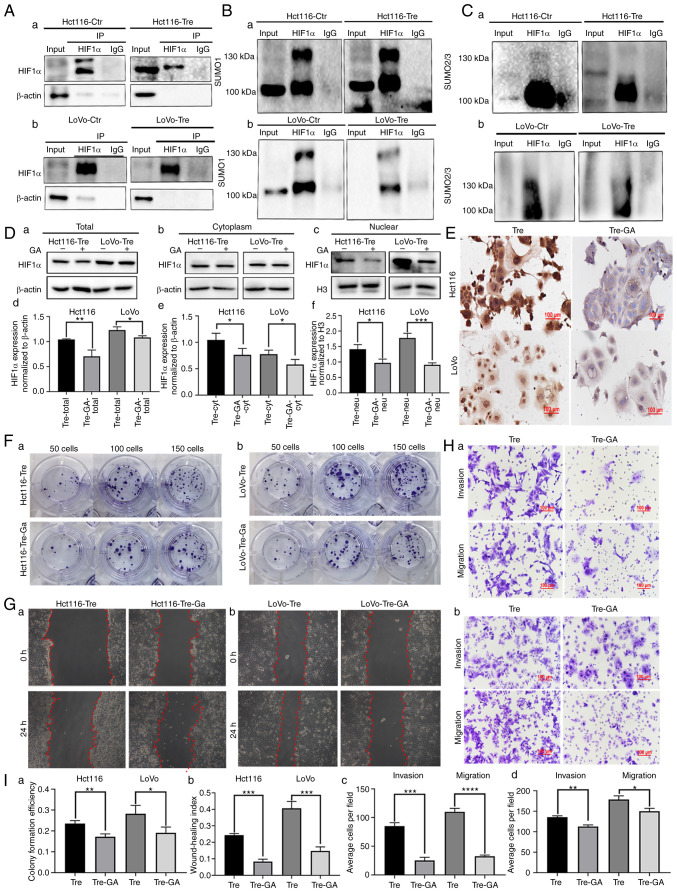
Figure 2.
The nuclear location of HIF1α modified by SUMOylation regulated the migration, invasion and proliferation of PDCs. (A) Results of HIF1α co-immunoprecipitation in (a) Hct116 and (b) LoVo PDCs (anti-HIF1α was used to perform immunoprecipitation). Total lysates of (a) Hct116 and (b) LoVo control cells and PDCs were immunoprecipitated with anti-HIF1α and immunoblotted with (B) anti-SUMO1 and (C) anti-SUMO2/3. (D) (a) Total, (b) cytoplasmic and (c) nuclear HIF1α expression in Hct116 and LoVo PDCs before and after 20 µM GA treatment. Statistical analysis of (d) total, (e) cytoplasmic and (f) nuclear HIF1α expression in Hct116 and LoVo PDCs befoer and after GA treatment. (E) Immunocytochemical staining of HIF1α in Hct116 and LoVo PDCs before and after GA treatment. (F) Colony formation of 50, 100 and 150 (a) Hct116 and (b) LoVo PDCs before and after GA treatment. (G) Wound-healing assay of (a) Hct116 and (b) LoVo PDCs before and after GA treatment at 0 h and 24 h (magnification, ×100). (H) The invasion and migration abilities of (a) Hct116 and (b) LoVo PDCs before and after GA treatment. (I) (a) The differences in colony formation efficiency of Hct116 and LoVo PDCs before and after GA treatment. (b) Statistical analysis of wound healing index of Hct116 and LoVo cells before and after GA treatment. (c) Comparison of the average cell number in invasion and migration assay of Hct116 PDCs before and after GA treatment. (d) Comparison of the average cell number in invasion and migration assay of LoVo PDCs before and after GA treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, ns, no significance. HIF1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha; PDCs, daughter cells; PGCCs, polyploid giant cells; GA, ginkgolic acid; Tre, PGCCs with PDCs; Ctr, control.