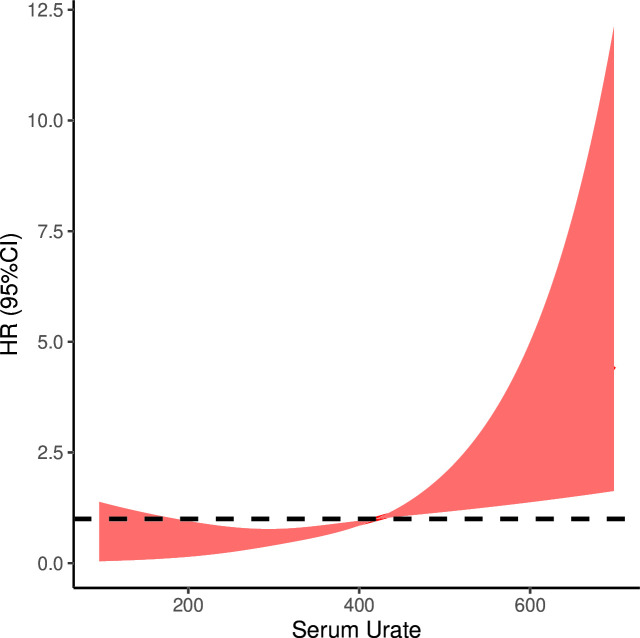
Figure 3.
The result of restricted cubic spline analysis. There was a significant non-linear dose–response relationship between the concentration of serum urate and the risk of COPD after adjusting potential confounding factors. Setting serum urate of 420 µmol/L as the reference (OR=1), the risk of COPD rapidly increased with the concentration of serum urate when it was higher than the reference. COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. HR, hazard ratio.