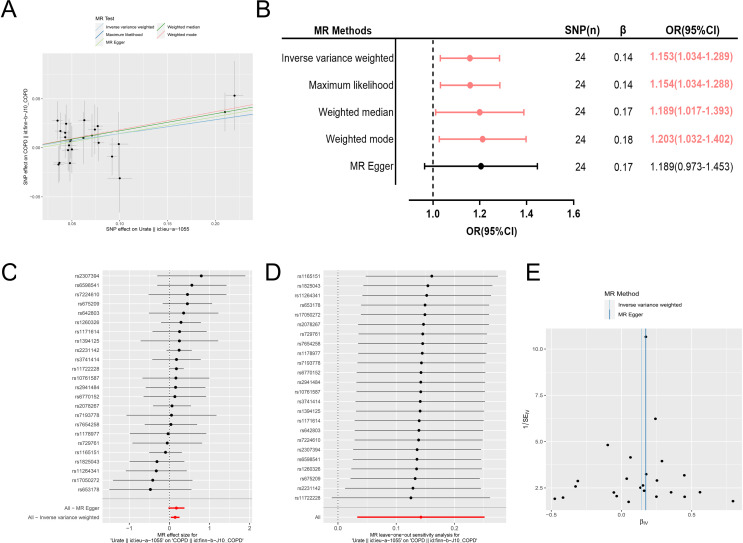
Figure 4.
(A–E) The results of univariable two-sample Mendelian randomisation (MR) analysis. (A) All five MR methods showed a positive effect of serum urate on COPD. (B) The IVW method yielded a significant positive effect of serum urate on the risk of COPD, and the statistical results of three other methods also yielded the same significant positive effect. (C) The forest plot showed the positive effects of each IV on COPD. (D) Leave-one-out analyses indicated that the results were stable and not driven by any single SNP. (E) The funnel plot showed a symmetrical distribution of the point estimate of the positive association effect, and this result indicated that the underlying bias was unlikely to affect the positive association. COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; IV, instrumental variable; IVW, inverse variance weighted; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.