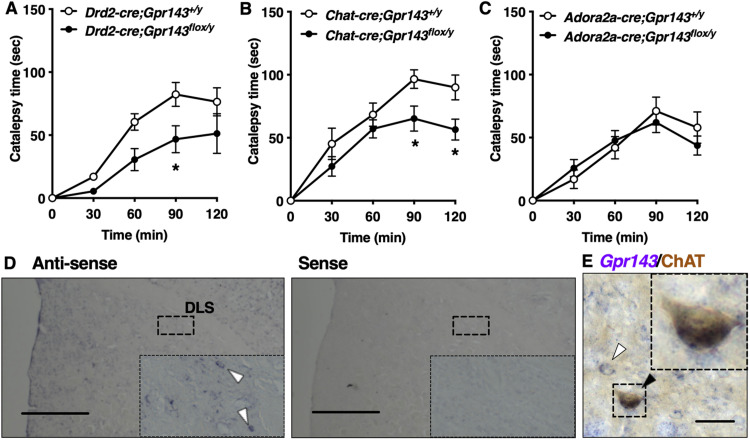
Figure 3.
Haloperidol-induced catalepsy is attenuated in DRD2-cre (+); Gpr143flox/y mice and ChAT-cre (+); Gpr143flox/y mice. A–C, Time course of catalepsy after treatment with haloperidol in (A) Drd2-cre(+);Gpr143flox/y, (B) ChAT-cre; Gpr143flox/y, and (C) Adora2a-cre; Gpr143flox/y mice and corresponding control mice (F(1,14) = 7.753, p = 0.015 in Drd2-cre;Gpr143flox/y, F(1,14) = 5.064, p = 0.041 in ChAT-cre; Gpr143flox/y, F(1,12) = 0.058, p = 0.814 in Adora2a-cre; Gpr143flox/y, n = 6–9). *P < 0.05, **p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. All values are the mean ± standard error of the mean. D, In situ hybridization signals for Gpr143 mRNA using anti-sense (left) and sense (right) probes in the dorsal striatum. Scale bar, 500 µm. Boxed areas indicate magnified images. E, Gpr143 mRNA (purple) and ChAT immunoreactive (brown) signals in the dorsolateral striatum of a Wt mouse. Black and white arrowheads indicate Gpr143-positive/ChAT-positive and Gpr143-positive/ChAT-negative neurons, respectively. Boxed areas indicate magnified images. Scale bar, 30 µm.