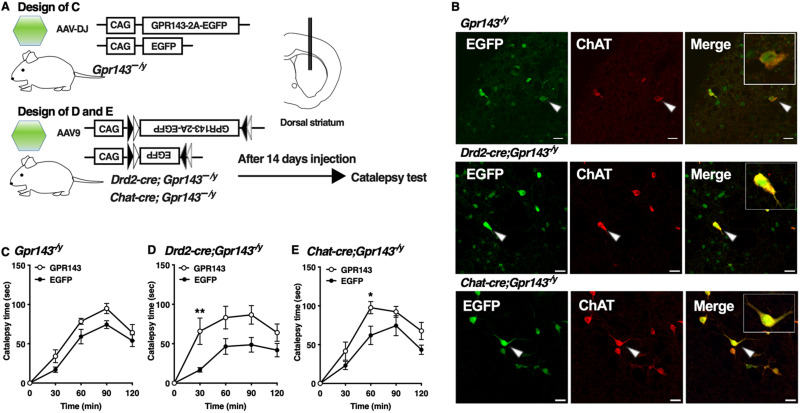
Figure 4.
Re-expression of GPR143 in cholinergic interneurons of the dorsal striatum prolongs haloperidol-induced catalepsy. A, Experimental design of the rescue of GPR143. B, EGFP (green), ChAT (red), and merged signals in the dorsolateral striatum of Gpr143−/y (upper), Drd2-cre;Gpr143−/y (middle), and ChAT-cre;Gpr143−/y (lower) mice infected with AAV-DJ-GPR143-P2A-EGFP or AAV9-DIO-GPR143-P2A-EGFP. The EGFP signals (arrowhead) were merged with ChAT-positive signal. Scale bar, 30 µm. C, Time course of catalepsy after treatment with haloperidol in Gpr143−/y mice infected with AAV-DJ-GPR143-P2A-EGFP (GPR143) or -EGFP in the dorsal striatum (F(1,15) = 6.863, p = 0.019, n = 8∼9). D, E, Time course of catalepsy after treatment with haloperidol in “(D) Drd2-cre;Gpr143−/y and (E) Chat-cre; Gpr143−/y mice infected with AAV9-DIO-GPR143-P2A-EGFP (GPR143) or DIO-EGFP in the dorsal striatum. (F(1,10) = 8.611, p = 0.015 in Drd2-cre;Gpr143−/y, F(1,11) = 17.94, p = 0.001 in ChAT-cre; Gpr143−/y, n = 6–7). *P < 0.05,**p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. All values are the mean ± standard error of the mean. n.s. indicates not significant.