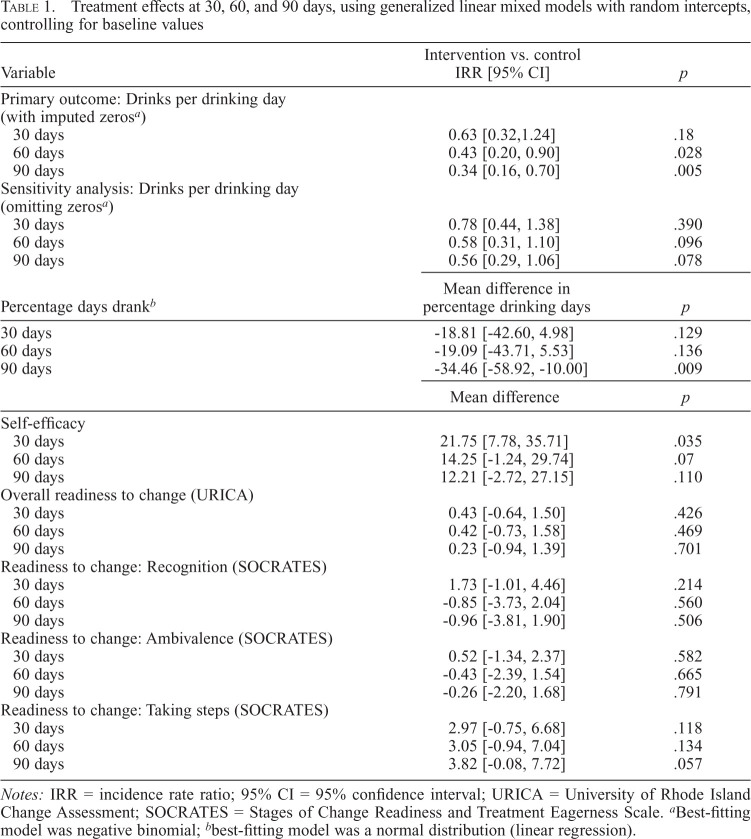
Table 1.
Treatment effects at 30, 60, and 90 days, using generalized linear mixed models with random intercepts, controlling for baseline values
| Variable | Intervention vs. control IRR [95% CI] | p |
|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome: Drinks per drinking day (with imputed zerosa) | ||
| 30 days | 0.63 [0.32,1.24] | .18 |
| 60 days | 0.43 [0.20, 0.90] | .028 |
| 90 days | 0.34 [0.16, 0.70] | .005 |
| Sensitivity analysis: Drinks per drinking day (omitting zerosa) | ||
| 30 days | 0.78 [0.44, 1.38] | .390 |
| 60 days | 0.58 [0.31, 1.10] | .096 |
| 90 days | 0.56 [0.29, 1.06] | .078 |
| Percentage days drankb | Mean difference in percentage drinking days | p |
|---|---|---|
| 30 days | -18.81 [-42.60, 4.98] | .129 |
| 60 days | -19.09 [-43.71, 5.53] | .136 |
| 90 days | -34.46 [-58.92, -10.00] | .009 |
| Mean difference | p | |
|---|---|---|
| Self-efficacy | ||
| 30 days | 21.75 [7.78, 35.71] | .035 |
| 60 days | 14.25 [-1.24, 29.74] | .07 |
| 90 days | 12.21 [-2.72, 27.15] | .110 |
| Overall readiness to change (URICA) | ||
| 30 days | 0.43 [-0.64, 1.50] | .426 |
| 60 days | 0.42 [-0.73, 1.58] | .469 |
| 90 days | 0.23 [-0.94, 1.39] | .701 |
| Readiness to change: Recognition (SOCRATES) | ||
| 30 days | 1.73 [-1.01, 4.46] | .214 |
| 60 days | -0.85 [-3.73, 2.04] | .560 |
| 90 days | -0.96 [-3.81, 1.90] | .506 |
| Readiness to change: Ambivalence (SOCRATES) | ||
| 30 days | 0.52 [-1.34, 2.37] | .582 |
| 60 days | -0.43 [-2.39, 1.54] | .665 |
| 90 days | -0.26 [-2.20, 1.68] | .791 |
| Readiness to change: Taking steps (SOCRATES) | ||
| 30 days | 2.97 [-0.75, 6.68] | .118 |
| 60 days | 3.05 [-0.94, 7.04] | .134 |
| 90 days | 3.82 [-0.08, 7.72] | .057 |
Notes: IRR = incidence rate ratio; 95% CI = 95% confidence interval; URICA = University of Rhode Island Change Assessment; SOCRATES = Stages of Change Readiness and Treatment Eagerness Scale.
Best-fitting model was negative binomial;
best-fitting model was a normal distribution (linear regression).