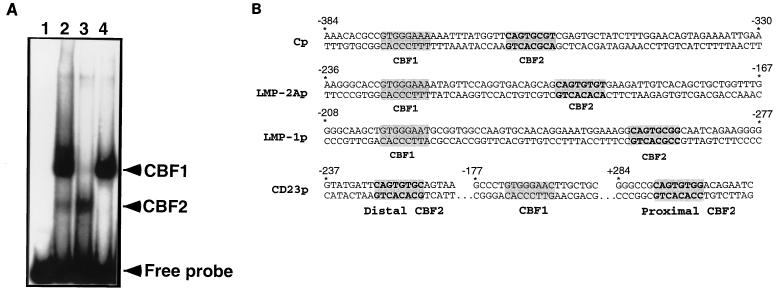
FIG. 2.
CBF1 and CBF2 bind distinct sequences in the Cp EBNA2 enhancer which are conserved in other EBNA2-responsive promoters. (A) Nuclear extracts from CA46 cells were incubated with a radiolabeled Cp sequence from positions −330 to −430 in the presence or absence of competitor oligonucleotides and analyzed by EMSA. Lanes: 1, probe only; 2, CA46 extract; 3, CA46 extract and cold 30-mer oligonucleotide competitor from positions −359 to −388 (CBF1 binding element); 4, CA46 extract and cold 30-mer oligonucleotide competitor from positions −339 to −368 (CBF2 binding element). (B) Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of EBNA2-responsive promoters and locations of their putative conserved CBF2 binding sequences. Shown also is the location of the CBF1 binding sites previously characterized in these promoters. The LMP-1 promoter (LMP-1p) contains in its natural context the consensus CBF1 binding site in the antisense orientation and is shown on top as the reverse complement strand to aid in the comparison of similarities. LMP-2Ap, LMP-2A promoter; CD23p, CD23 promoter.