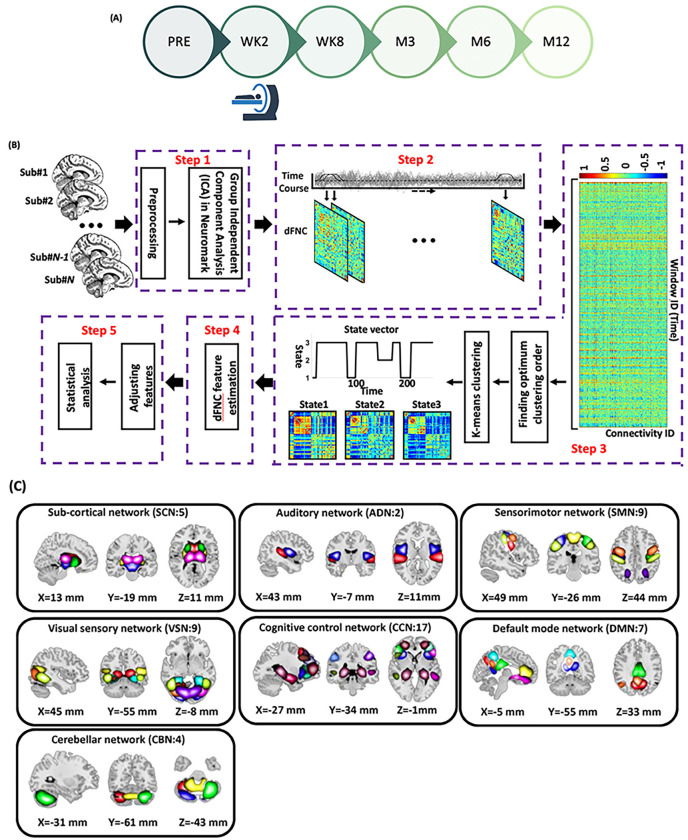
Figure 1. Data collection procedure and analytic pipeline:
A) The PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5) was utilized to evaluate PTSD symptoms at various time points, encompassing pre-trauma (PRE), week 2 (WK2), week 8 (WK8), month 3 (M3), month 6 (M6), and month 12 (M12). During the study visit at WK2 a subgroup of participants underwent MRI scans, either in the morning or the afternoon. B) Dynamic functional network connectivity (dFNC) analytic pipeline: Step 1: Initially, the time-course signal of 53 intrinsic connectivity networks (ICNs) was identified through group-ICA in the Neuromak template. Step 2: Subsequently, the identified 53 ICNs were subjected to a taper sliding window segmentation to calculate FNC. Each subject yielded 201 FNCs, each with a size of 53 × 53. Additionally, static FNC was computed for the entire recording duration. Step 3: To cluster the FNCs into three distinct groups, the FNC matrices were vectorized and concatenated, followed by the utilization of k-means clustering with correlation as the distance metric. Step 4: From the state vector, occupancy rate (OCR) was computed for each subject, resulting in a total of three OCR features for each subject. Step 5: In order to investigate the relationship between OCRs with the PTSD clinical measure (i.e, PCL-5), we used GLM to compute the associations, taking into account factors such as age, sex, years of education, scanning site, income, marital status, employment status, and percentile ADI. The resulting t-statistics from this analysis were then converted to correlation (r) values. C) We utilized the NeuroMark pipeline to extract robust intrinsic connectivity networks (ICNs), totaling 53 components, which demonstrate consistent replication across independent datasets. These 53 distinct components were initially identified through group-ICA analysis using the NeuroMark template. These components were subsequently categorized into seven distinct networks, which include the subcortical network (SCN), auditory network (AND), visual sensory network (VSN), sensorimotor network (SMN), cognitive control network (CCN), default mode network (DMN), and cerebellar network (CBN).