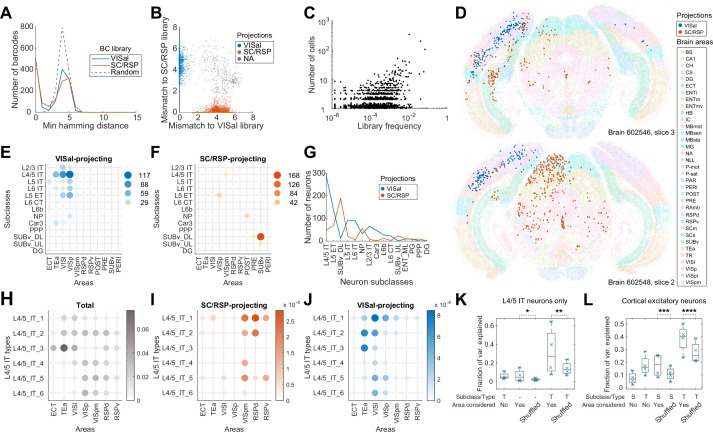
Figure 4. Multiplexed retrograde labeling recapitulates known cortical projections.
(A) Histograms showing the distribution of the minimum Hamming distance between each barcode and all other barcodes for barcodes in the VISal library (blue), the SC/RSP library (red), and random barcodes (dashed). (B) The distribution of mismatch between each sequenced barcode and the closest barcode in the CCS library (y axis) or in the non-CCS library (x axis). Colors indicate which library each barcode was mapped to. Gray cells did not match to either library, likely because the libraries were not sequenced to completion. (C) The frequencies of barcodes in the libraries (x axis) are plotted against the number of sequenced cells carrying those barcodes (y axis). Jitter is added on the y-axis to help visualize overlapping dots. (D) Two representative slices, one from each brain showing all sequenced cells on each slice. Barcoded cells are color-coded by projections and non-barcoded cells are color-coded by brain regions. (E-F) The number of neurons from each cortical area and each subclass that projected to either VISal (E) or SC/RSP (F). Dot size and colors indicate the number of cells. (G) The distribution of the number of projecting cells (y axis) for each subclass (x axis). (H)-(J) The fractions of the indicated L4/5 IT types in each cortical area (H) and the fraction of those that project to SC/RSP (I) or VISal (J). (K-L) Fractions of variance in the probability of projections explained by combinations of the compositional profiles of cell types (S: subclass, T: type, -: cell type was not used) with or without considering cortical areas (Area considered) for L4/5 IT neurons (K) or for all excitatory neurons (L). Boxes indicate median and quartiles, and whiskers indicate range of data. Each point (N = 4) indicate data from different slides, each containing two slices. *p=6 × 10–70, **p=6 × 10–58, ***p=7 × 10–78, ****p=6 × 10–37 comparing the means to 100 iterations of shuffled controls using two-tailed t-tests.