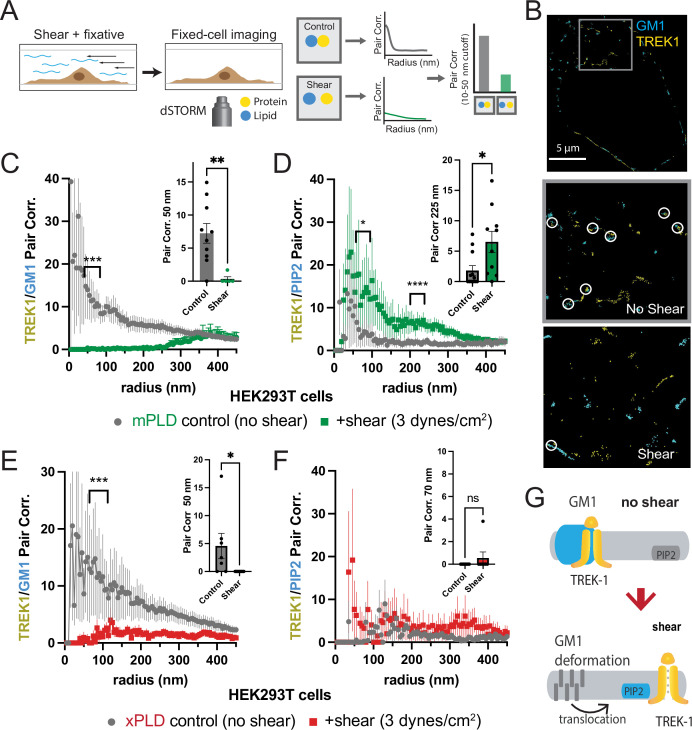
Figure 2. Shear induces nanoscopic movement of TREK-1 in HEK293T cells.
(A) Schematic representation of the shear fixing protocol. Cells grown in a shear chamber are fixed while shear force is applied. Fixed samples are then labeled with fluorescent antibodies or CTxB and subjected to imaging for nanoscopic movement (<250 nm) by two-color super-resolution imaging and pair correlation (Pair corr.). (B) EGFP-STORM imaging of TREK-1:EGFP and Alexa 647 cholera toxin B (CTxB) with and without shear in HEK293T cells. The middle panel, outlined in gray, is a zoomed portion of the cell surface outlined in the top panel. The bottom panel is a zoomed portion of the cell surface from a cell treated with shear (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1I for full image). Locations of TREK-1/GM1 proximity are outlined with a white circle. (C) Pair correlation analysis (Pair corr.) of TREK-1 with GM1 lipids before and after shear (3 dynes/cm2; green) determined by EGFP-STORM imaging when mouse phospholipase D2 (mPLD2) is overexpressed (non-permeabilized). The significance of the Pair corr. change is shown across the range of radii 50–70 nm (along the curve) and at a single 50 nm radius (inset). (D) Combined EGFP-STORM imaging of TREK-1 with Alexa 647-labeled PIP2 in the presence of overexpressed mPLD2 (permeabilized). Significance is shown for radii 70–85 nm along the curve and at a single 225 nm radius (inset). (E, F) Combined EGFP-STORM of TREK-1 in the presence of catalytically inactive PLD2 (xPLD2). Shear (3 dynes/cm2) of TREK-1 is shown as a red curve with xPLD2 present. The experiments are as described in panels (C) and (D). In (E) a significant shift in TREK-1/GM1 Pair corr. is shown for 50–70 nm (along the curve) and at a 50 nm radius (inset). In (F) Pair corr. did not appear to shift significantly, as determined by a Student’s t-test or for multiple point a nested Student’s t-test; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. (G) Cartoon illustrating the association of TREK-1 with GM1 lipids prior to shear (top) and with PIP2 lipids (bottom) in response to mechanical shear (red arrow).