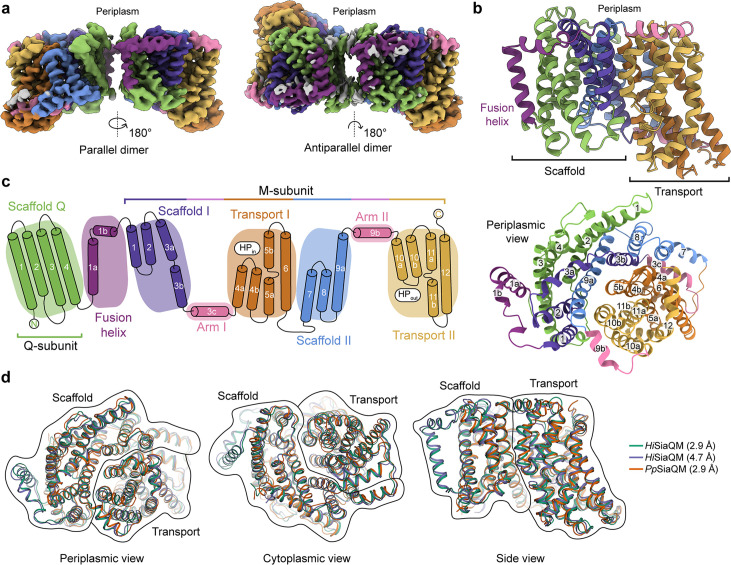
Figure 2. The structure of HiSiaQM.
(a) Coulomb maps for the parallel (3.36 Å) and antiparallel (2.99 Å) HiSiaQM homodimers. The periplasmic surfaces of the monomers are facing the same direction for the parallel dimer (PDB: 8THI), whereas the periplasmic surface of one monomer is rotated 180° for the antiparallel dimer (PDB: 8THJ). The transport domain (orange and gold) is in the ‘elevator down’ conformation in all four monomers. The dimeric interface in both maps is distanced and neither has significant protein–protein interactions. The maps are coloured according to the topology in (c). Density consistent with phospholipids is coloured grey and is particularly present in the dimer interface of the higher resolution antiparallel dimer map. (b) Structural model of the HiSiaQM monomer. The transport domain is in the ‘elevator down’ conformation with the substrate-binding site facing the cytoplasm. (c) The topology of HiSiaQM is the same as the non-fused PpSiaQM with the addition of the fusion helix. The M-subunit forms the transport domain (orange and gold) and bracing arm helices (pink) as well as a large portion of the scaffold (purple and blue). The Q-subunit is entirely used as a scaffold for the elevator transport mechanism. The fusion helix (purple) connects the scaffold and adds to its size. It also forms a short horizontal helix, similar to the arm helices of the M-subunit. (d) A structural overlay of HiSiaQM (2.9 Å structure, green; 4.7 Å structure, purple) and PpSiaQM (2.9 Å structure, orange) shows that the helices of the structures are well aligned, and all three structures are in the same conformation.