Fig. 2:
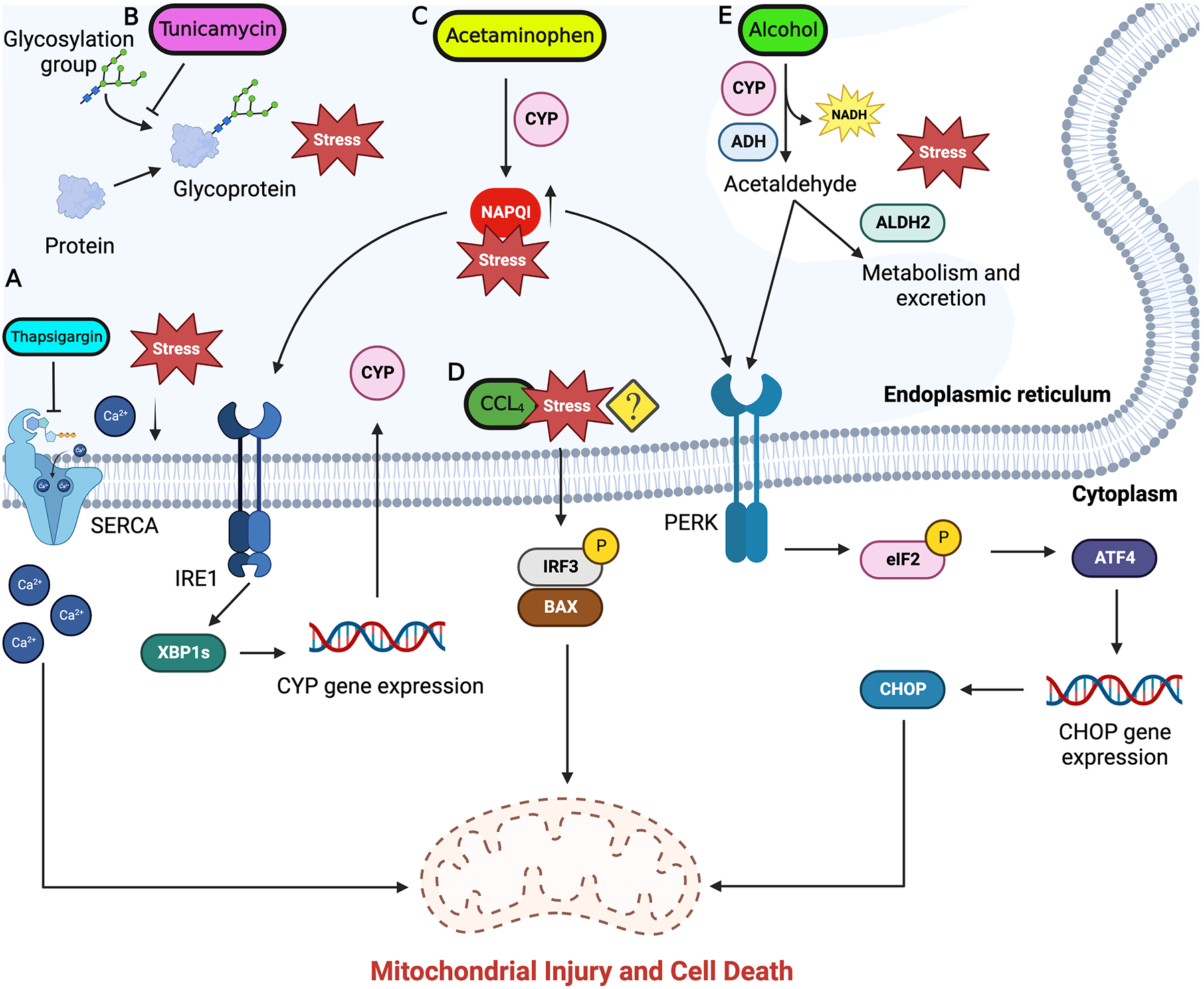
ER stress response signal flow in chemical induced liver injury. Subthreshold level concentrations of hepatotoxicants like acetaminophen, alcohol, CCl4 are metabolized by the ER resident enzymes. Buildup of these toxins beyond the threshold levels is associated with induction of ER stress. A) Thapsigargin inhibit SERCA pump on ER membrane and unbalance the ER calcium homeostasis and induce ER stress. B) Tunicamycin inhibits protein glycosylation and protein assembly causing accumulation of unfolded proteins resulting in activation of ER stress. C) Toxic levels of acetaminophen result in accumulation of reactive intermediate NAPQI triggering ER stress through IRE1 and PERK branches. D) The mechanism of ER stress induction by CCl4 is still not completely understood but is seen to activate apoptosis through IRF3 and BAX. E) Alcohol imbalances ER redox balance and trigger ER stress through PERK which induces ISR and subsequent CHOP expression. Downstream signaling from UPR activate mitochondria mediated apoptosis in hepatocytes which can progress to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Figure generated using BioRender.com.
