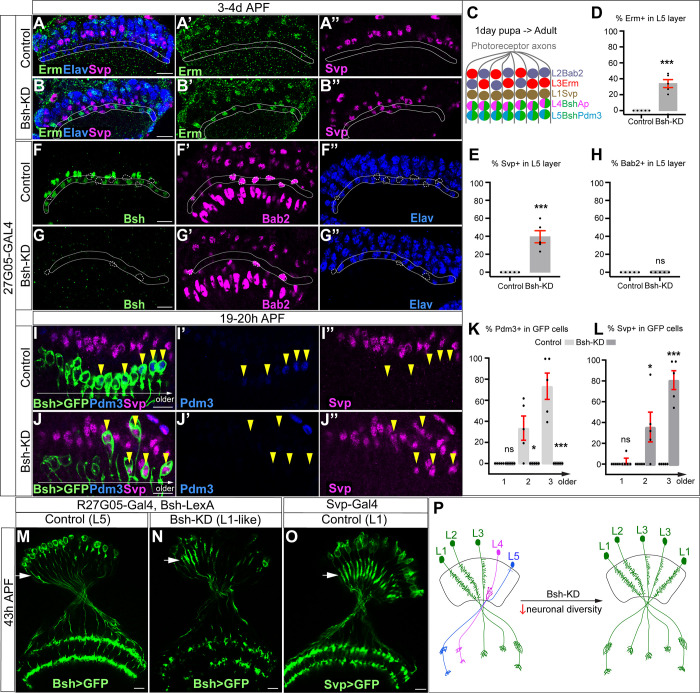
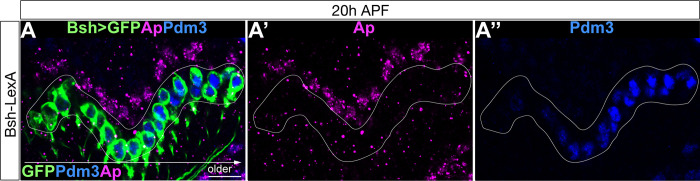
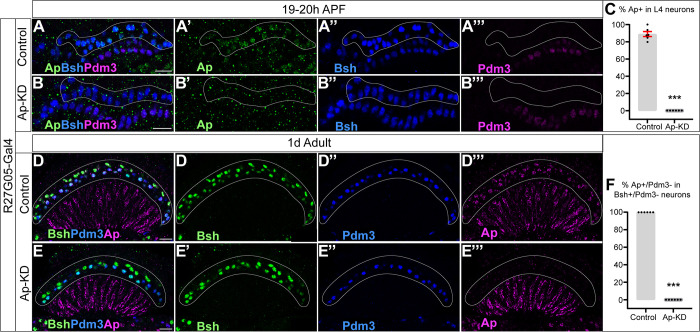
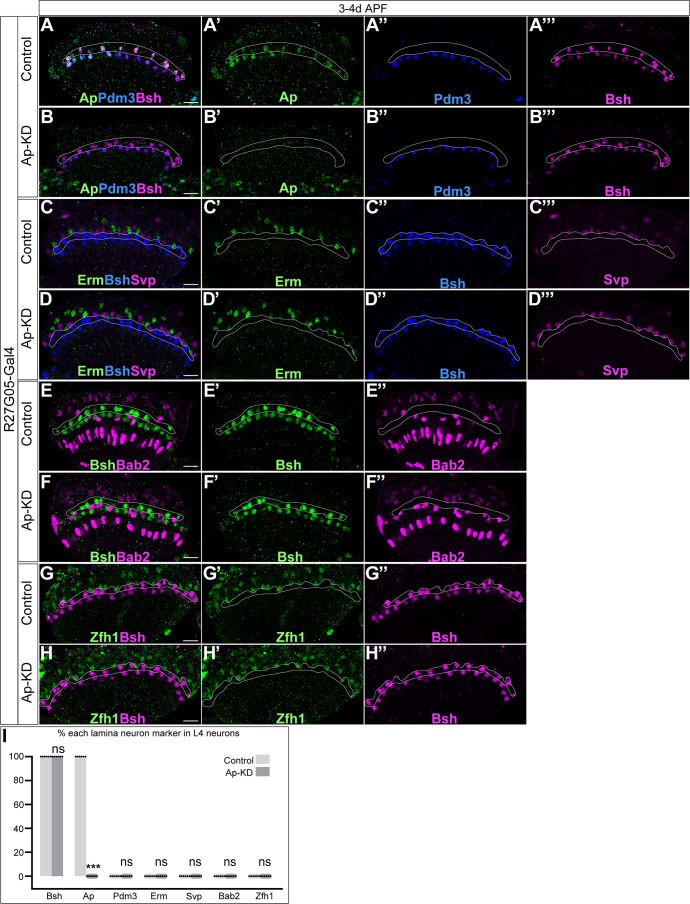
Figure 3. Bsh suppresses L1/L3 neuronal fate.
(A–E) Bsh-knockdown (KD) in lamina progenitor cells (LPCs) results in the ectopic expression of the L1 marker Svp and L3 marker Erm in L4/L5 cell body layers (circled). (C) Schematic of lamina neuron development from 1-day pupae to adult. (D and E) Quantification of Erm and Svp expression. Here and below, scale bar, 10 µm. (F–H) Bsh-KD in LPCs does not produce ectopic Bab2-positive neurons or glia in the L5 layer (circled). n≥5 brains. Genotype: R27G05-Gal4>UAS-Bsh-RNAi. (H) Quantification of Bab2 expression. (I–L) Bsh-KD in LPCs results in ectopic Svp+ L1 neurons at the expense of Pdm3+ L5 neurons. Bsh GFP+ neurons marked with yellow arrowheads show L1 marker Svp expression in Bsh-KD while L5 marker Pdm3 expression is in control. Genotype: Bsh-LexA>LexAop-GFP. (K and L) Quantification of Pdm3 and Svp expression. (M–O) Bsh-KD transforms L5 neuron morphology to L1-like neuronal morphology. (M) Control L5 neurons have very few dendrites in the lamina neuropil. Genotype: R27G05-Gal4, Bsh-LexA>LexAop-GFP. (N) Bsh-KD transforms L5 neuron morphology to L1-like neuronal morphology. Genotype: R27G05-Gal4>UAS-Bsh-RNAi; Bsh-LexA>LexAop-GFP. (O) Control L1 neurons show bushy dendrites throughout the lamina. Genotype: svp-Gal4, R27G05-FLP>UAS-FRT-stop-FRT-myrGFP. (P) Summary. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Each dot represents each brain. n=5 brains in (D), (E), (H), (K), and (L). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns = not significant, unpaired t-test.