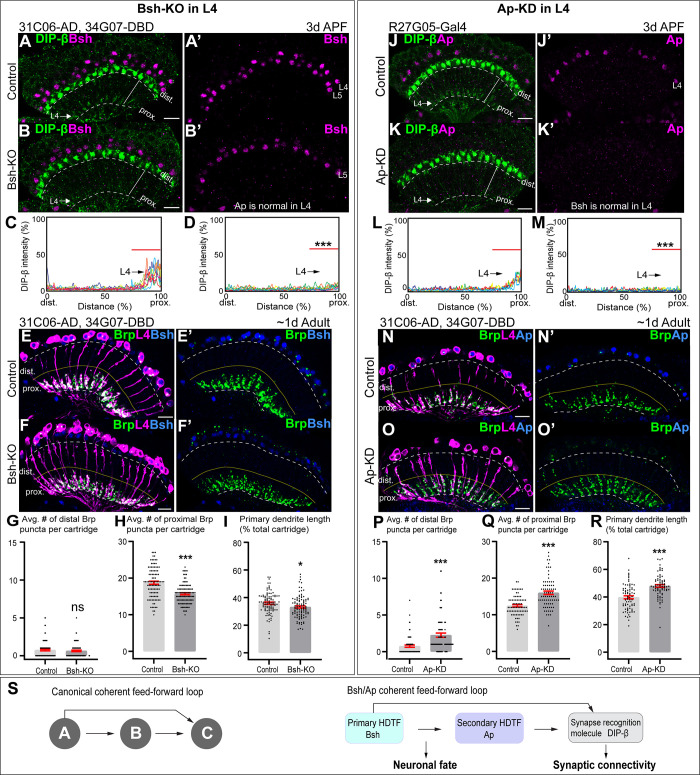
Figure 6. Bsh and Ap form a coherent feed-forward loop to activate DIP-β.
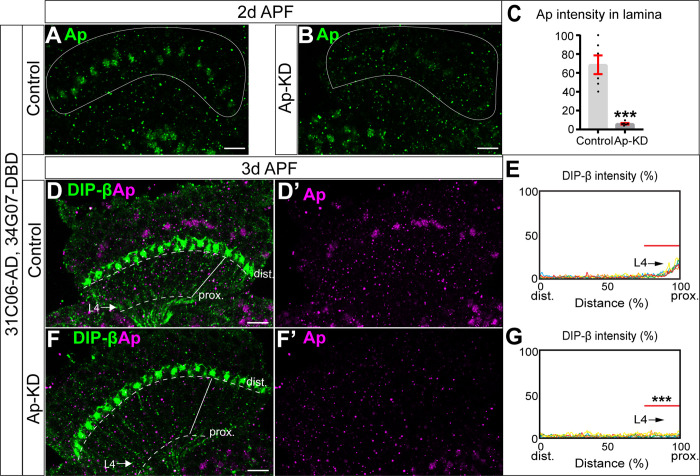
(A–D) Bsh Crispr knockout (KO) in postmitotic L4 neurons results in loss of DIP-β expression in the proximal lamina neuropil (arrow) at 3 days after pupa formation (APF). DIP-β expression is detected using an anti-DIP-β antibody. The signal in the distal lamina is from non-lamina neurons, probably LawF. Significantly reduced DIP-β fluorescence intensity is observed in the proximal lamina (75–100% distance, marked by red bar (C, D)). ***p<0.001, unpaired t-test, n=8 brains, each line represents each brain, scale bar, 10 µm. Genotype: 31C06-AD, 34G07-DBD>UAS-Cas9, UAS-Bsh-sgRNAs. (E–I) Bsh Crispr KO in L4 neurons results in a decrease of primary dendrite length and proximal synapse number in postmitotic L4 neurons of 1-day adults. Here and below, white dash lines indicate the lamina neuropil and yellow lines show the boundary between the distal and proximal lamina. The average number of Brp puncta in L4 neurons present within the distal or proximal halves of lamina cartridges. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ns = not significant, unpaired t-test, n=100 cartridges, n=5 brains, each dot represents one cartridge, data are presented as mean ± SEM. Genotype: 31C06-AD, 34G07-DBD>UAS-Cas9, UAS-Bsh-sgRNAs, UAS-myrGFP, UAS-RSR, 79C23-S-GS-rst-stop-rst-smFPV5-2a-GAL4. (J–M) Ap RNAi knockdown (KD) in postmitotic L4 neurons results in loss of DIP-β expression in the proximal lamina neuropil (arrow) at 3 days APF. The signal in the distal lamina is from non-lamina neurons, probably LawF. Significantly reduced DIP-β fluorescence intensity is observed in the proximal lamina (75%–100% distance, marked by red bar (L, M)). ***p<0.001, unpaired t-test, n=8 brains, each line represents each brain, scale bar, 10 µm. Genotype: R27G05-Gal4>UAS-ApRNAi. (N–R) Ap-KD in L4 neurons results in an increase of primary dendrite length and proximal synapse number in postmitotic L4 neurons in 1-day adults. The average number of Brp puncta in L4 neurons present within the distal or proximal halves of lamina cartridges. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ns = not significant, unpaired t-test, n=100 cartridges, n=5 brains, each dot represents one cartridge, data are presented as mean ± SEM. Genotype: 31C06-AD, 34G07-DBD>UAS-RSR, 79C23-S-GS-rst-stop-rst-smFPV5-2a-GAL4, UAS-Ap-shRNA, UAS-myrGFP. (S) Summary.