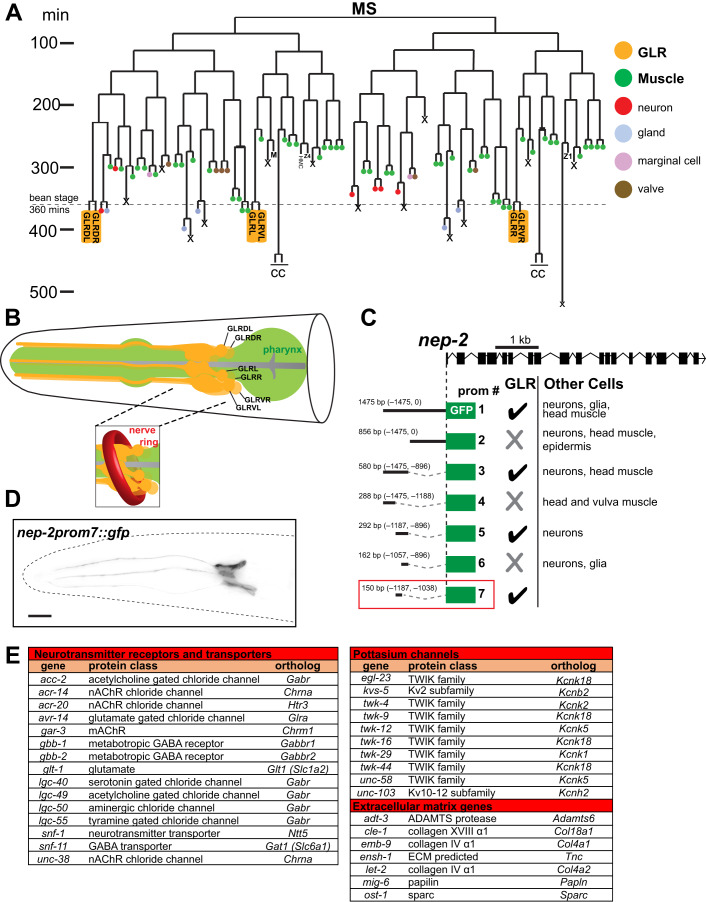
Figure 1. Generation of a GLR-specific driver to study the expression profile of the mesodermal GLR glia.
(A) GLR glia (yellow boxes) derive from the lineage of the blast cell MS. This lineage produces mainly body wall muscle and pharyngeal muscle cells (green). GLR glia (yellow) are born at around the embryonic bean stage (360 min of embryonic development). The HMC cell and coelomocytes (CC) also derive from the MS lineage. Schematic adapted from (Sulston et al, 1983). (B) Schematic representation of the GLR glia (yellow). Pharynx is shown in green. The inset shows how C. elegans Nerve Ring (red) wraps around the sheet-like GLR glia processes. Schematic redrawn and modified from (Altun and Hall, 2016). (C) Cis-regulatory dissection analysis for the gene nep-2 resulted in isolation of a GLR glia-specific driver, prom7 (red box). (D) Fluorescence image of an L4 C. elegans showing expression of nep-2prom7::gfp specifically in GLR glia. Anterior is left, dorsal is up, and scale bar is 10 μm. (E) Genes from three families (neurotransmitter receptors and transporters, potassium channels and extracellular matrix genes) are overrepresented among GLR-enriched genes.