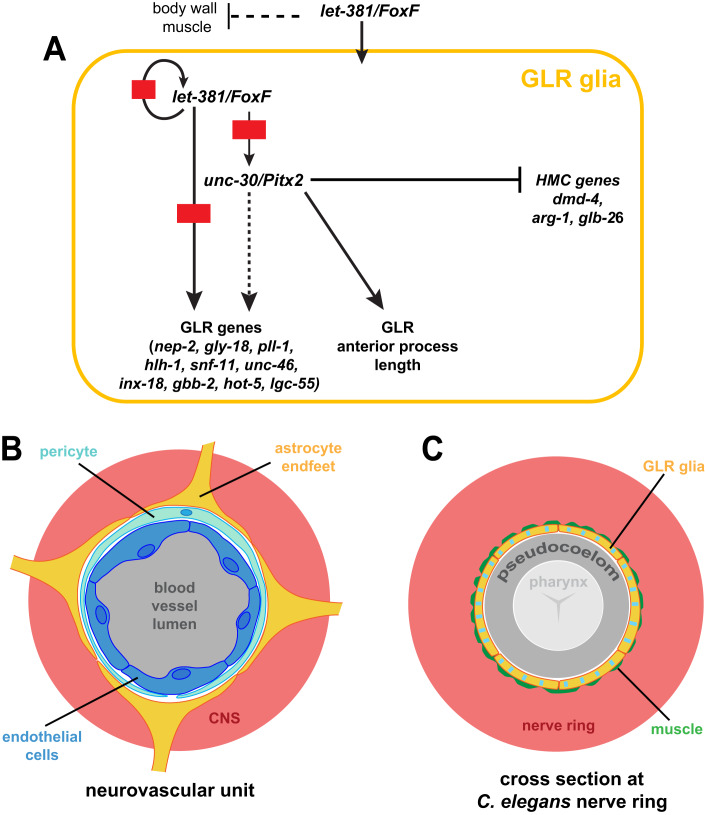
Figure 10. Regulatory network for the specification and identity maintenance of the C. elegans GLR glia.
(A) Schematic of the regulatory network identified in this study controlling fate specification and differentiation of GLR glia. (B) At the neurovascular unit, endothelial cells (dark blue), pericytes (light blue), and astrocytic endfeet (yellow) form the Blood–Brain Barrier isolating the central nervous system (CNS—red) from blood circulation (gray). (C) Similarly, the GLR glia sheet-like processes (yellow with blue stripes to show a mixed astrocytic-endothelial/mural fate) isolate the C. elegans nerve ring (red) from the pseudocoelom (gray). A thin layer of head muscle arms (green) penetrates the C. elegans nerve ring and therefore GLR flat processes are in close proximity to head neuromuscular junctions (White et al, 1986). The pseudocoelom is shown larger than its actual volume.