FIGURE 2.
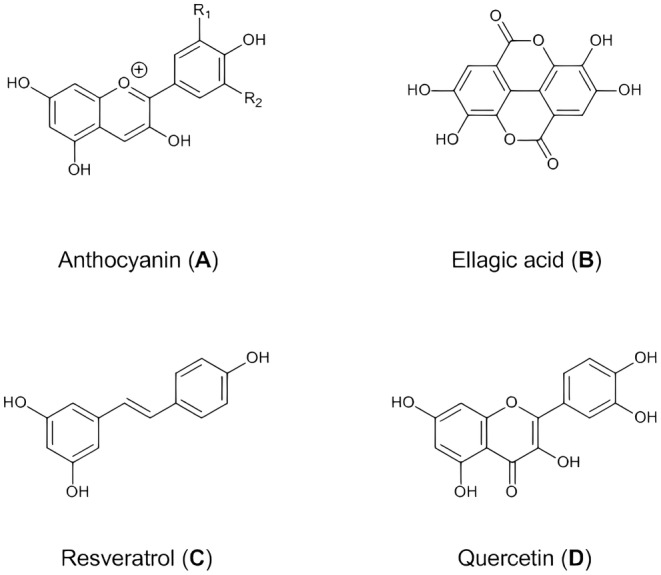
Molecular structure of natural compounds. (A) A C6‐C3‐C6 skeleton primarily characterizes the fundamental structure of anthocyanin. The molecule consists of an anthocyanidin core, hydroxyl groups, sugar moiety, and acyl groups. (B) Ellagic acid is a polyphenolic compound with a molecular formula C14H6O8. It comprises a fused ring system comprising two benzene rings and a lactone ring. (C) The combination of the stilbene backbone, hydroxyl groups, and possible methoxy group defines the molecular structure of resveratrol. (D) The combination of benzene rings, oxygen atoms, hydroxyl groups, double bonds, and the ketone group defines the molecular structure of quercetin.
