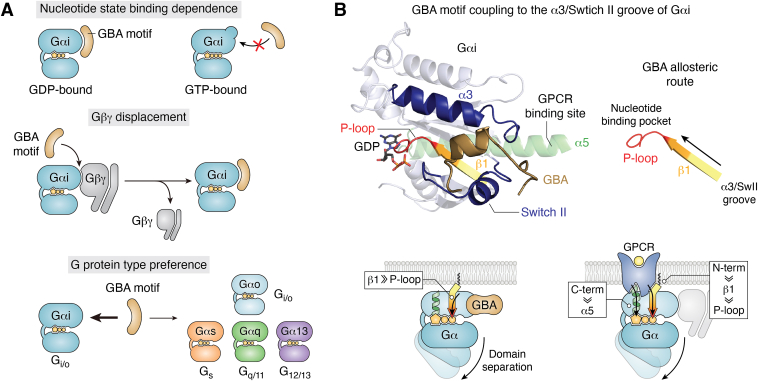
Figure 2.
Molecular and structural basis for the action of GBA motifs on G proteins.A, specific features of the interaction between GBA motifs and Gαi subunits. GBA motif binds preferentially to inactive over active Gα subunits and can displace Gβγ from preformed heterotrimers in the absence of nucleotide exchange. GBA motifs bind primarily to Gai isoforms, whereas it binds weakly to other members of the Gi/o family or of other G protein families. B, GBA motifs bind to the groove formed between the α3 helix and the switch II in Gαi, which is communicated allosterically to the P-loop in the nucleotide binding pocket via the β1 strand. The binding site of GBA motifs of Gα does not overlap with that of GPCRs, but the allosteric routes that communicate with the nucleotide binding pocket might be partially shared between GPCRs and GBA motifs. GBA, Gα-binding-and-activating; GIV, Gα-interacting vesicle-associated protein; GPCR, G protein–coupled receptor.