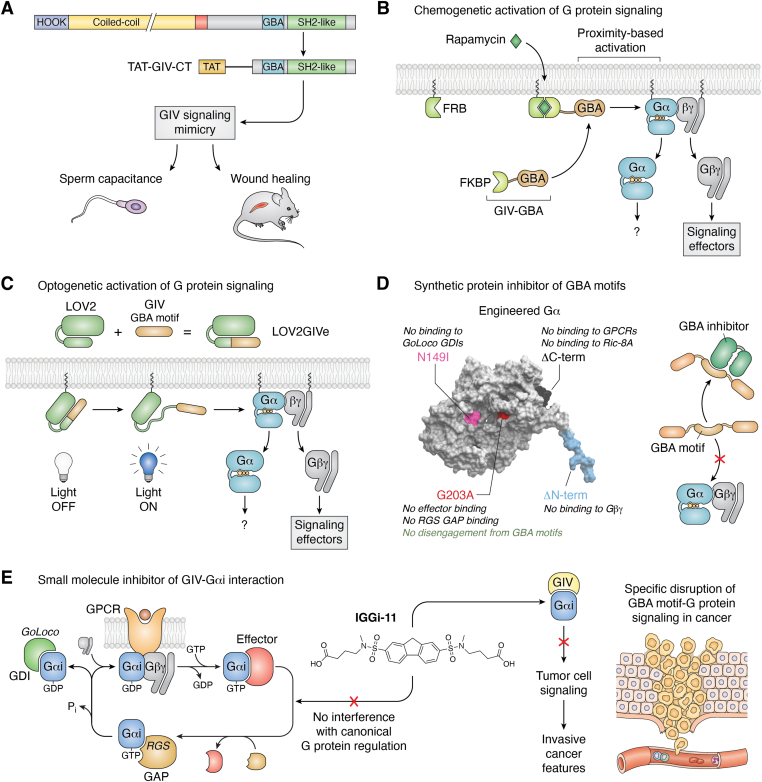
Figure 4.
Tools to leverage or investigate signaling mediated by GBA motifs.A, TAT-fused C-terminal region of GIV (TAT-GIV-CT) can be delivered to cells as a cell-penetrating protein that mimics the signaling activity of GIV. TAT-GIV-CT has been shown to increase human sperm capacitance and skin wound healing in mice. B, chemogenetic control of the subcellular localization of GBA motifs allows to control G protein signaling activation in cells. C, fusing a GBA motif to the light-sensitive LOV2 domain of Avena sativa (LOV2GIVe) allows for optogenetic control of G protein signaling in cells. D, an engineered Gα subunit that constitutively binds to GBA motifs but does not bind to other G protein regulators and effectors serves as genetically encoded “GBA inhibitor” (GBAi). E, a small molecule that binds to Gαi named IGGi-11 competitively inhibits signaling mediated by GIV–Gαi complexes in cancer without affecting canonical mechanism of G protein signaling mediated by GPCR and downstream pathway effectors and regulators. GBA, Gα-binding-and-activating; GBAi, GBA inhibitor; GIV, Gα-interacting vesicle-associated protein; GPCR, G protein–coupled receptor; IGGHi-11, inhibitor of the GIV–Gαi interaction; TAT, transactivator of transcription.