FIGURE 1.
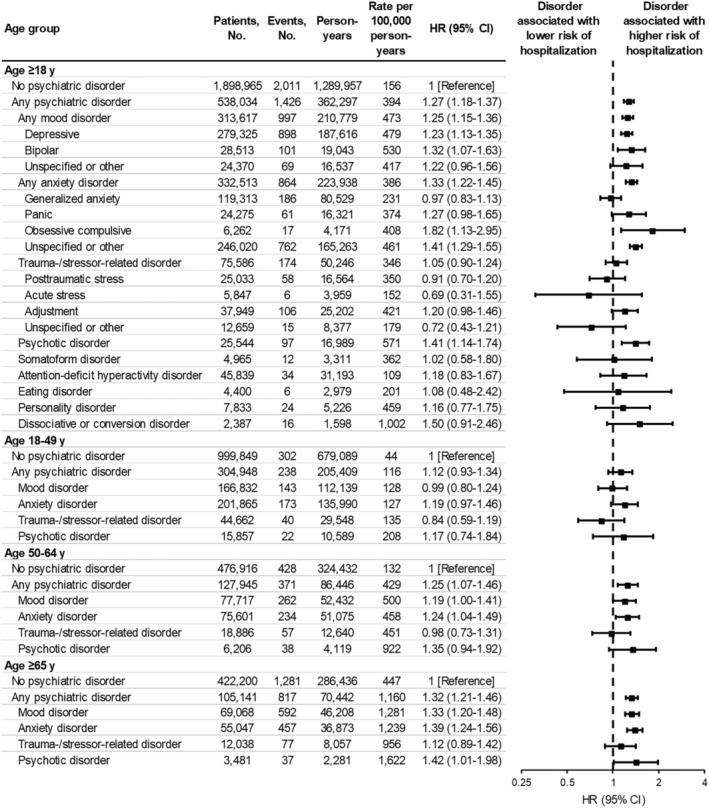
Associations between psychiatric disorders and COVID‐19‐associated hospitalization, stratified by age group. A hazard ratio (HR) > 1.0 indicates that the respective psychiatric disorder was associated with a higher risk of COVID‐19‐associated hospitalization. Each HR was obtained from a separate model comparing patients with the respective psychiatric disorder (any, mood, anxiety, trauma‐stressor‐related, or psychotic) to patients with no psychiatric disorder. HRs were adjusted for site, age (natural spline with four knots), sex (male, female, unknown), race and ethnicity (Asian, Black, Hispanic, White, other, unknown), Medicaid coverage (yes, no, unknown), underlying respiratory condition (yes, no), underlying non‐respiratory condition (yes, no), number of underlying medical conditions (square‐root transformed), number of SARS‐CoV‐2 test records documented in the patient's electronic medical record prior to the start of the study period (0, 1, 2–4, ≥5), and time‐varying mRNA COVID‐19 vaccination status (unvaccinated, two doses 14–149 days earlier, two doses ≥150 days earlier, three doses 7–119 days earlier, three doses ≥120 days earlier, four doses 7–59 days earlier, four doses ≥60 days earlier). CI, confidence interval.
