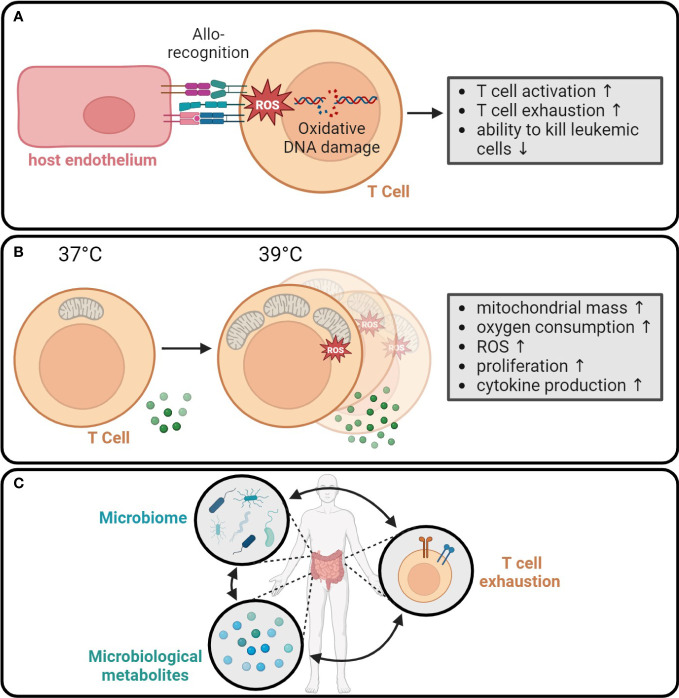
Figure 5.
Systemic metabolic events regulate anti-tumor immunity. (A) Allorecognition leads to the production of ROS in T cells. The resulting oxidative DNA damage enhances short-term T cell activation, while increasing the T cell exhaustion and reducing the ability to kill tumor cells (204). (B) Fever causes an increase in mitochondrial mass, oxygen consumption, and ROS production in T cells. Moreover, the proliferation and cytokine production are enhanced at 39°C compared to 37°C (206). (C) Microbiome and secreted immunomodulatory metabolites interact with circulating T cells and probably contribute to T cell exhaustion (207).