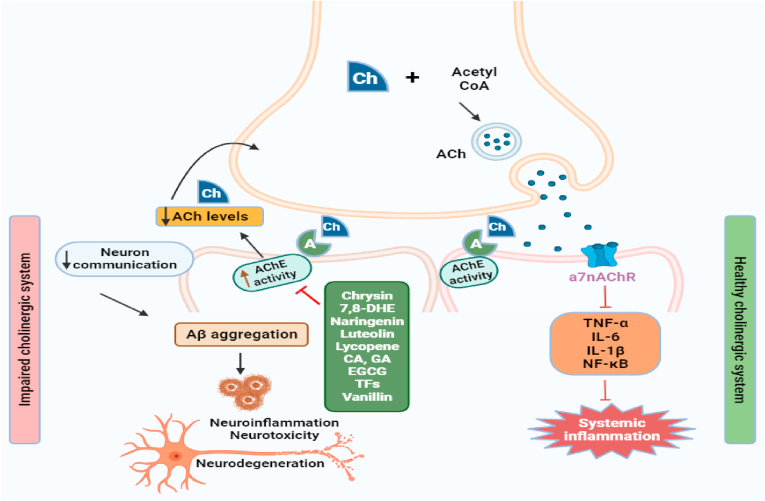
Fig. 2.
Illustration of dietary small molecules inhibiting/reducing the AChE activity in cholinergic pathway involved in AD pathogenesis. Acetylcholine after being synthesized is released from the vesicles and supports memory formation. AChE causes the breakdown of acetylcholine. So, dietary small molecules like chrysin, 7.8-DHE, naringenin, luteolin, lycopene, CA, GA, EGCG, TFs, and vanillin are blocking AChE thus preventing acetylcholinesterase breakdown, Aβ aggregation, neuroinflammation, and supporting memory formation. Ach: acetylcholine; Aβ: amyloid beta; AchE: acetylcholinesterase; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-6: interleukin-6; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B.