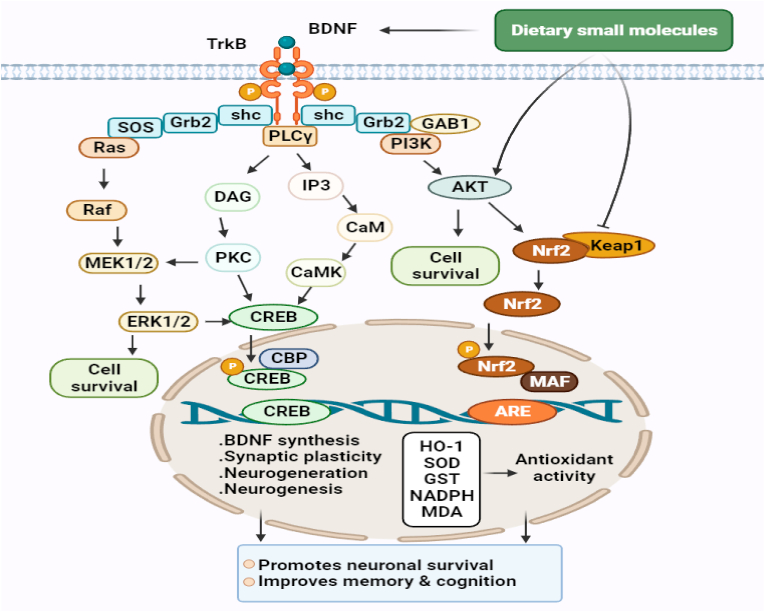
Fig. 3.
Molecular pathways are involved in the neuroprotective, antioxidant, and promoting neuronal cell survival of dietary small molecules. The PI3K/Akt pathway destabilizes Nrf2-Keap1 complex, which under basal conditions leads to the ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2 by proteasomal system, and thus, promotes the nuclear translocation of Nrf2. This, in turn, activates the Nrf2-ARE antioxidant system and results in the expressions of multiple genes that encode antioxidant enzymes responsible for redox metabolism and GSH synthesis and metabolism. Activated Akt also regulates cell survival by maintaining a balance between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins. Furthermore, MAPK signaling pathways regulate neuronal survival and the transcriptions of CREB-dependent genes that encode BDNF, and other proteins required for synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis. Dietary small molecules may promote cell survival by activating TrkB signaling by functioning as BDNF mimetics or by promoting Akt phosphorylation or inhibiting Nrf2-Keap1 complex, and thus, activating the antioxidant defense system. TrkB signaling and the Nrf2-ARE antioxidant system are complementary to each other, and simultaneous activation of these pathways has been shown to confer neuroprotection against oxidative stress and to attenuate memory and cognition impairments in patients with AD or NDDs brain injury. BDNF: brain derived neurotrophic factor; CREB: cAMP response element-binding protein; TrkB: tropomyosin receptor kinase; Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; HO-1: heme oxygenase 1; (PI3K)/AKT: phosphoinositol 3-kinase; SOD: superoxide dismutase; GST: glutathione-S-transferase; MDA: malondialdehyde; ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; CaMK: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; PKC: protein kinase-C.