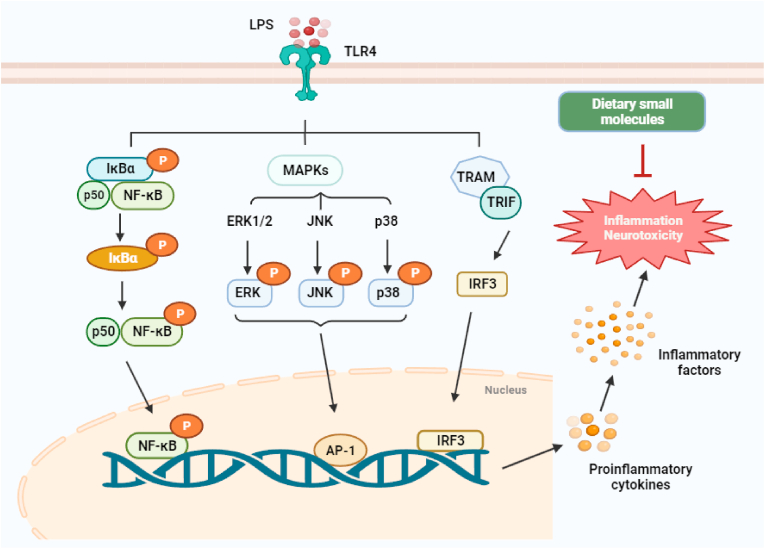
Fig. 5.
Molecular pathways are involved in the anti-inflammatory effect of dietary small molecules. LPS is a potent activator of the NF-кB, MAPK, and IRF3 signaling pathways. Phosphorylation of IкB by IKK results in the release of cytoplasmic NF-кB and subsequently its translocation into the nucleus. In the nucleus, NF-кB activates the expression of the pro-inflammatory gene. NF-кB can also be activated by MAPK and IRF3 signaling pathways. Dietary small molecules mainly inhibit the secretion and expression of related inflammatory factors through multiple molecular pathways. LPS: lipopolysaccharide; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; p38: NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase.