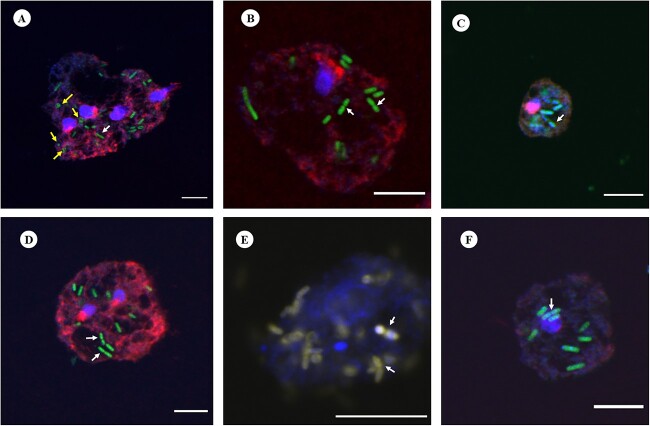
Figure 6.
Representative FISH micrographs showing the presence of intracellular bacteria in Acanthamoeba trophozoites investigated in this study. Probes EUK516 conjugated with Cy5, targeting Acanthamoeba, and EUB conjugated with Cy3, targeting most of bacterial strains were used for all Acanthamoeba strains positive for bacterial 16S rRNA. DAPI was used in mounting medium when visualized by a fluorescence microscope. Probe pB-914 labelled with 6-FAM was used for isolates containing high abundance of bacteria belong to Enterobacteriaceae family. (A) Rod shaped bacteria were observed throughout the cytoplasm of Acanthamoeba trophozoites (Indian corneal isolate) and a few cocci bacteria were also observed (yellow arrows). The white arrow represents bacterium cell undergoing binary fission. (B) Bacteria showing binary fission (white arrows) in vacuole like structure of Acanthamoeba recovered from water sample (R3). (C and D) Corneal isolates of Acanthamoeba spp. (Ac-112 and L-579/20, respectively) with intracellular bacteria. (E) Intracellular bacteria labelled with probes EUB and pB-914 simultaneously in Acanthamoeba sp. isolated from an AK patient. (F) Clinical (Ac-102) isolate of Acanthamoeba trophozoite depicting rod shaped intracellular bacteria. Indicators: white arrow, bacterial cell undergoing binary fission; yellow arrow: cocci shaped bacteria. Scale bar in each panel represents 10 μm.