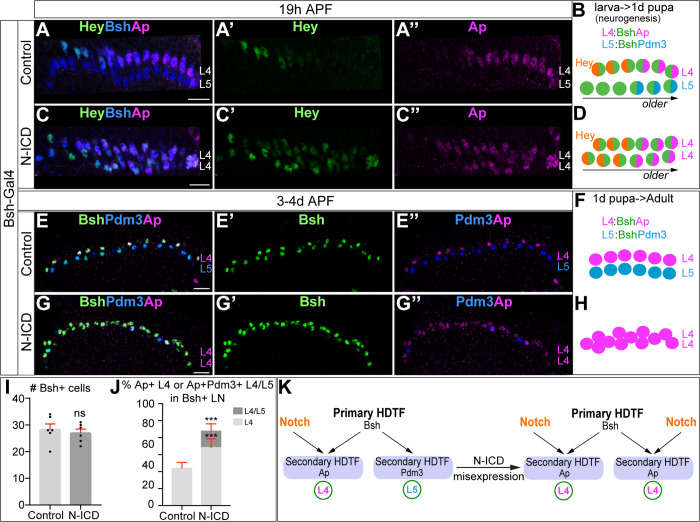
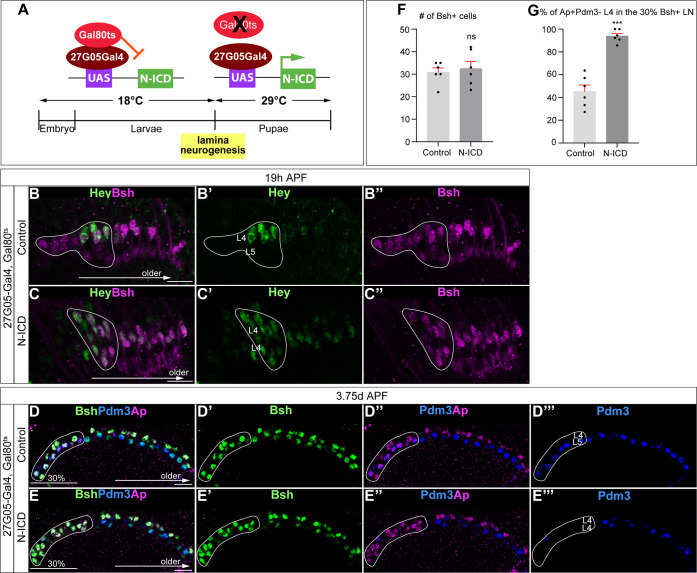
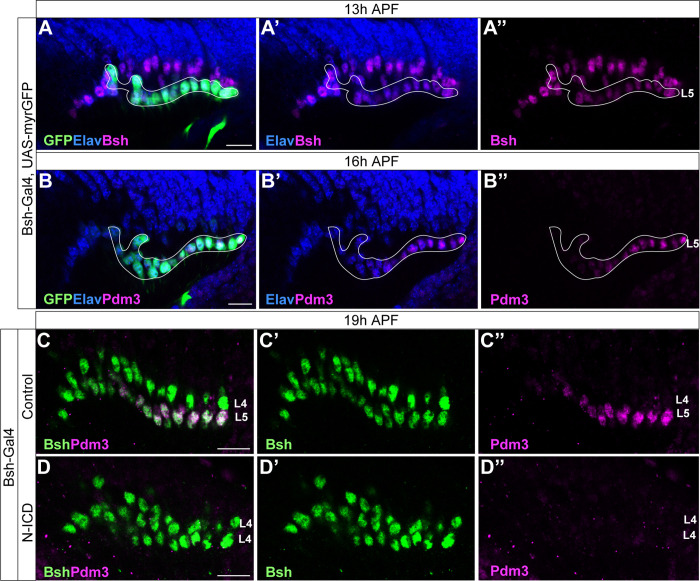
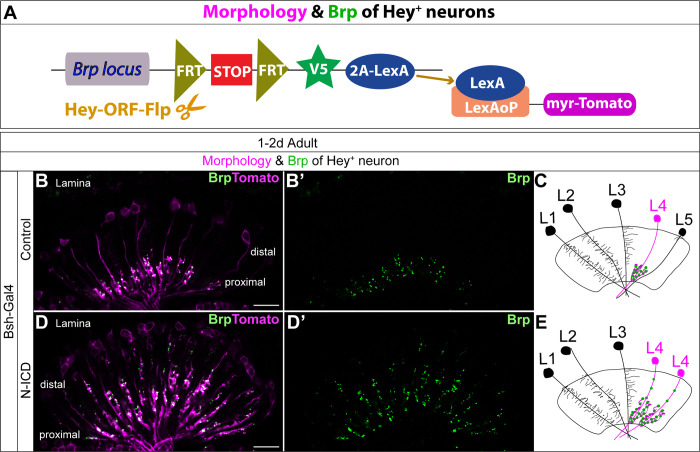
Figure 4. Bsh with Notch signaling activates Ap and specifies L4 neuronal fate.
(A–D) Ectopic expression of N-ICD in newborn L5 neurons (Bsh-Gal4 >UAS-N-ICD) results in ectopic Hey and Ap activation and an increased number of L4 neurons at 19 hr APF. Here and below, scale bar, 10 µm, n≥5 brains. (E–J) N-ICD shows Bsh+ lamina neurons are mainly Ap+ L4 neurons, though the number of Bsh+ lamina neurons remains unaffected at 3-4d APF. (I–J) Quantification (single optical section). (K) Summary. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Each dot represents each brain. n=6 brains in (I), (J). ***p<0.001, ns = not significant, unpaired t-test.