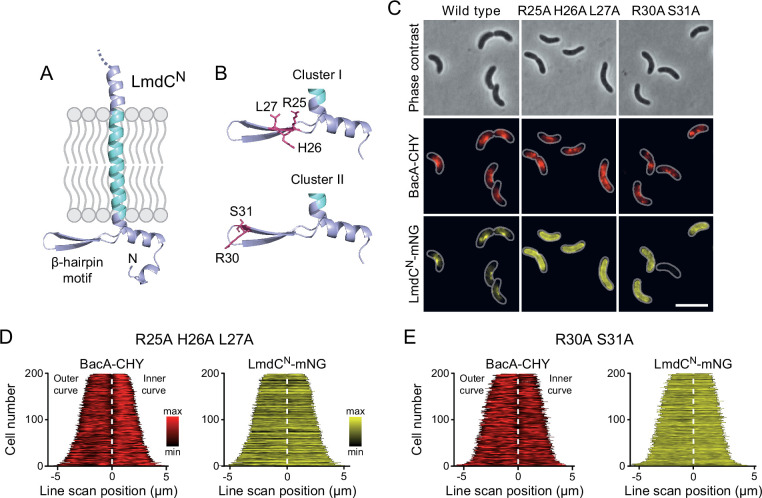
Figure 11. The β-hairpin in the cytoplasmic region of LmdC is critical for BacA binding.
(A) Predicted structure of LmdCN, comprising the first 80 amino acids of LmdC. The transmembrane domain is colored light blue. The cytoplasmic domain includes a conserved β-hairpin motif. (B) Clusters of amino acids mutated for the analysis of BacA-LmdC interaction. Mutated amino acids are shown as red sticks. (C) Localization of BacARs-CHY and the indicated LmdCNRs-mNG variants in the ΔlmdCRs background. The Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient (PCC) of the two fluorescence signals in a random subpopulation of cells is 0.914 for the wild-type fusion protein (SP119), 0.887 for the R25A-H26A-L27A variant (SP237) and 0.827 for the R30A-S31A variant (SP238). Scale bar: 5 µm. (D,E) Demographs showing the distribution of BacA-mCherry and (D) R25A-H26A-L27A variant (SP237) or R31A-S31A variant (SP238) of LmdCN-mNG along the outer and inner curve of the cell (n=200 cells per strain). The white line marks the point of transition from the outer and the inner curve. The analysis was performed as described in Figure 10F.