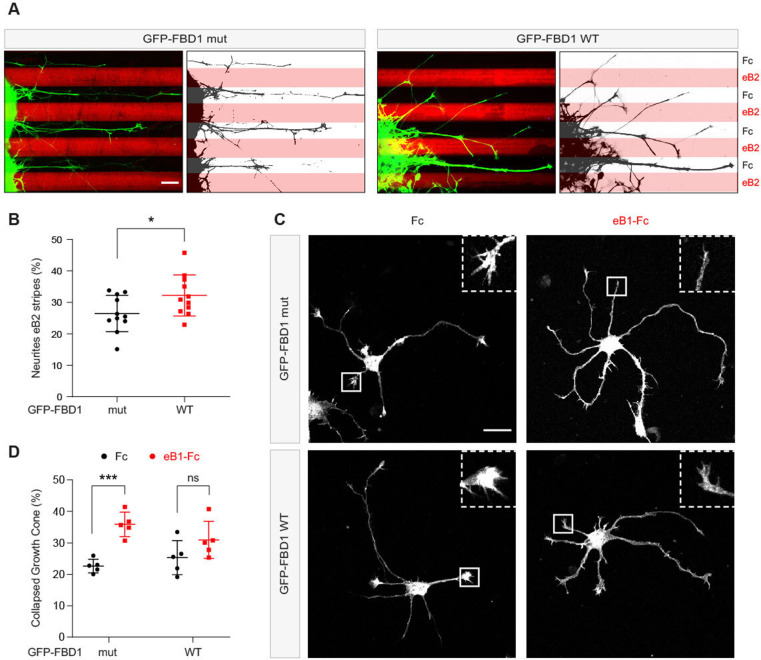
Figure 7. Exogenous FBD1 overexpression impairs EPH receptor functions in chick spinal cord explants and mouse hippocampal neurons.
(A) Representative images of ephrin-B2 stripe assays with chick embryonic spinal cord explants overexpressing GFP-FBD1 mut (negative control) or GFP-FBD1 WT. Images with inverted GFP signal in dark pixels on Fc / eB2 (pink) stripes are placed beside the original images. Scale bar is 50 μm. (B) Quantification of GFP-positive neurites present on ephrin-B2 stripes (GFP-FBD1 mut vs. GFP-FBD1 WT, p=0.0410, two-tailed unpaired t-test). (C) Representative images of DIV2 mouse hippocampal neurons overexpressing GFP-FBD1 mut or GFP-FBD1 WT and challenged with Fc control or ephrin-B1 (eB1-Fc). Scale bar is 20 μm. (D) Quantification of growth cone collapse rate for hippocampal neurites. GFP-FBD1 mut: Fc vs. eB1-Fc, p=0.0006; GFP-FBD1 WT: Fc vs. eB1-Fc p0.1341. Two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test. Error bars represent SD.