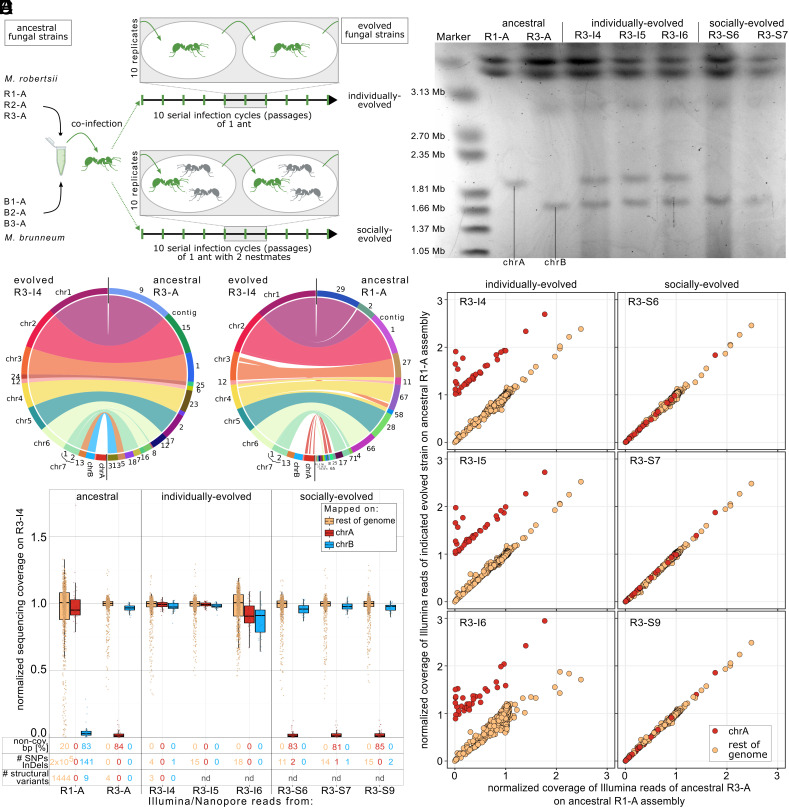
Fig. 1.
Multiple independent transfers of accessory chrA from the ancestral M. robertsii R1-A to evolved M. robertsii R3 during experimental co-infection of an ant host. (A) Experimental procedure of the selection experiment performed by Stock et al. (35). Argentine ants were exposed (green) to a mix of six strains—three M. robertsii and three M. brunneum—and kept either alone (individual treatment, n = 10 replicate lines) or with two nestmates (gray; social treatment, n = 10 replicate lines). The produced infectious spores were used to expose ants in 10 serial infection cycles as described in ref. 35. We here performed whole genome sequencing of the six ancestral and the individually and socially evolved strains at the end of the experiment. (B) Synteny blot of the nanopore-based assemblies of the evolved R3-I4 compared to the two ancestral R1-A and R3-A. Accessory chrA is missing in R3-A but shows synteny to contigs in R1-A. (C) Normalized Illumina sequencing coverage mapped on the evolved R3-I4 nanopore-based assembly in 50 kb windows for chrA (red), chrB (blue), and the rest of the genome (yellow). The fraction of genomic compartments lacking a single sequencing read (non-cov. bp) and the number of SNPs/InDels absent in the ancestral R3-A strain are given. The number of structural variants (≥50 bp) determined by nanopore reads mapped onto the R3-I4 nanopore-based assembly is indicated (nd = nondetermined, as no nanopore reads were available for these samples). (D) PFGE image of small chromosomes from the ancestral R1-A and R3-A, as well as all three individually evolved and two socially evolved R3 strains. All three independent individually evolved R3 strains contained both chrA and chrB. (E) Normalized sequencing coverage comparison of Illumina reads mapped on the ancestral R1-A nanopore-based assembly in 50-kb windows. Only 50-kb windows that are syntenic to chrA of R3-I4 exhibited changes in sequencing coverage in the three individually evolved R3 strains, indicating that no other genetic material was transferred to them from the ancestral R1-A. Note: The plots exclude the rDNA cluster for clarity, due to its high coverage.