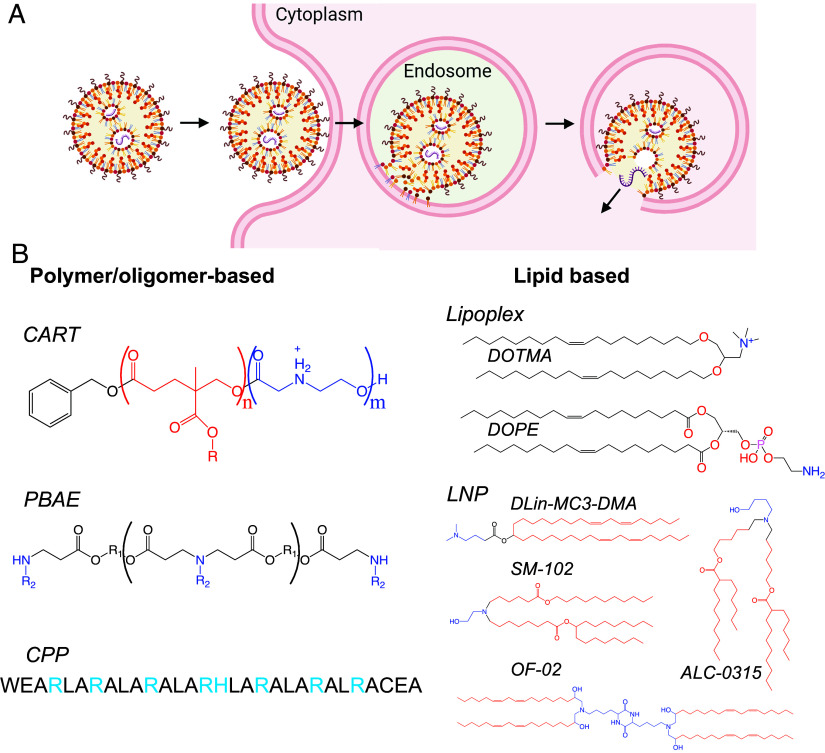
Fig. 1.
(A) Overview of nanoparticle RNA delivery. RNA must be encapsulated in the nanoparticle, endocytosed, and escape the endosome into the cytoplasm. Generated by BioRender.com. (B) Sample of polymeric and lipid-based RNA nanoparticle delivery materials, lipid tails in red and cationic or ionizable components in blue. R groups for charge-altering releasable transporters (CARTs) and poly(beta-amino ester) PBAEs indicate structural flexibility that can be tuned via high-throughput screening; for cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), structural optionality is not explicitly shown, but hundreds of CPPs for delivery of various cargos have been described (25). Lipid-based delivery can use ionizable lipid-free lipoplexes, such as those containing DOTMA and DOPE, while LNPs contain ionizable lipids with examples given here. DLin-MD3-DMA is FDA approved in a liver siRNA delivery formulation, and SM-102 and ALC-0315 are used in the Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech COVID mRNA vaccines, respectively. OF-02 is highly potent for liver mRNA delivery lipid and illustrates the structural diversity of ionizable lipids.